ISRAEL - UAE PEACE AGREEMENT
2020 AUG 18
Mains >
International relations > India and Global Regions > India & West Asia
WHY IN NEWS:
- The Israel–United Arab Emirates Peace Agreement or Abraham Accord, was agreed to by Israel and the UAE on August 13, 2020
BACKGROUND:
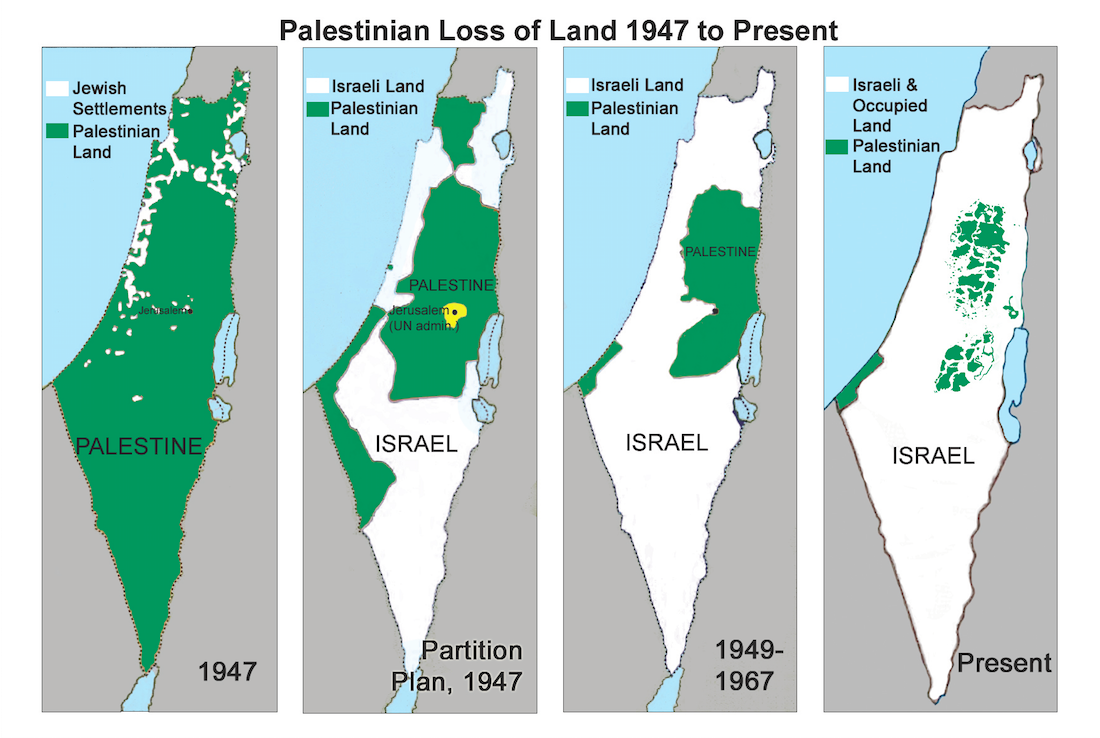
- Arab-Israeli relations have largely been conflict-ridden ever since the state of Israel was declared in 1948
- UAE is the third Arab country, after Egypt in 1979 and Jordan in 1994, to formally normalize its relationship with Israel, as well as the first Persian Gulf country to do so.
ABOUT THE ACCORD:
- UAE would recognise the state of Israel and establish formal diplomatic relations
- Talks on direct flights, security, telecommunications, energy, tourism and health care will be on.
|
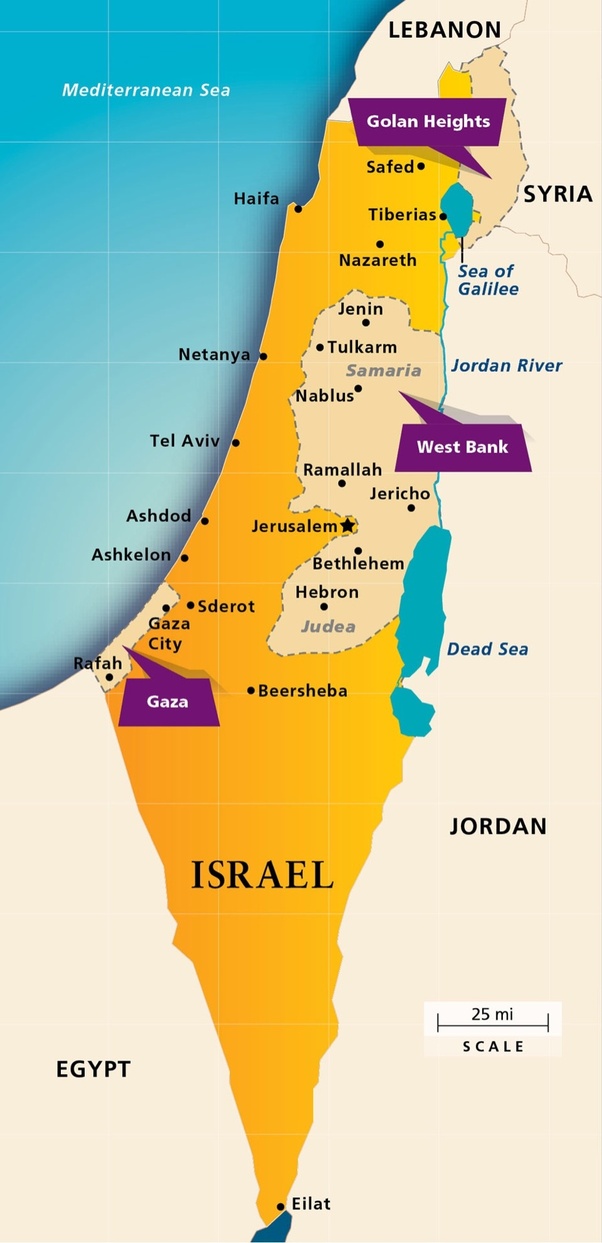
About West Bank:
The West Bank is sandwiched between Israel and Jordan.
One of its major cities is Ramallah, the de facto administrative capital of Palestine.
The West Bank also contains a significant section of the western Dead Sea shore.
Israel took control of it in the Six-day Arab-Israeli war, 1967 and has over the years established settlements there.
The territory is still a point of contention due to a large number of Palestinians who live there and hope to see the land become a part of their future state.
When Israel took control of the land in 1967 it allowed Jewish people to move in, but Palestinians consider the West Bank illegally occupied Palestinian land.
|
- Concurrently, Israel agreed to suspend plans for annexing parts of the West Bank.(not for any relaxation of the actual occupation)
- The agreement normalizes what had long been informal but robust foreign relations between the two countries
- An important component of the Abraham Accord, though not specifically spelled out, is enhanced security cooperation against regional threats, especially from Iran and its proxies
- Within the region, Bahrain, Egypt, Jordan, and Oman publicly welcomed the Abraham Accord. Saudi Arabia has remained silent
- Bahrain, Oman, Sudan and Morocco is most likely to follow the UAE
IMPACTS:
- Abraham Accord provides an opportunity for Israel and the Palestinians to renew negotiations to end their conflict.
- It will lead to suspension of annexation of areas in West Bank.
- Potential to change Arab-Israeli relations for good:
- It also shows how the Arab countries are gradually decoupling themselves from the Palestine question
- It could improve peace in West Asia
- Contain Iran:
- The Accord would pave the way for the region’s Sunni Arab kingdoms and the Jewish-majority Israel enhancing regional cooperation against their common foe, Shia Iran and the Lebanese militant group Hezbollah.
- The deal smoothens the UAE’s international campaign to be seen as a beacon of tolerance in the Middle East despite being governed by autocratic rulers.
- Economic development in the region:
- Opening direct ties between two of the Middle East’s most dynamic societies and advanced economics will transform the region by spurring economic growth, enhancing technological innovation and forging closer people-to-people relations.
- Better relation with U.S:
- The UAE stood to benefit from purchases of advanced American weapons systems that are available only to nations that are friendly to Israel.
ANALYSIS:
- Palestine’s concern:
- Agreement meant that Palestinians would think that UAE put its own interests before those of the Palestinians, who had always assumed that Arab countries would not sign peace treaties with Israel before the rights of Palestinians had been guaranteed.
- While the deal halts Israeli annexation plans, the Palestinians have repeatedly urged Arab governments not to normalize relations with Israel until a peace agreement establishing an independent Palestinian state is reached.
- Many countries such as Turkey, Iran and Pakistan criticized the deal as treason against the Palestinians
- The Accord is considered as a violation of the 2002 Arab Peace Initiative
- The Arab Peace Initiative, a Saudi Arabia initiative endorsed by the Arab League, offered recognition to Israel in exchange for its full withdrawal from the occupied territories.
- The Accord is a diplomatic victory for U.S, as it was successful in bringing two of its allies in to the peace table.
IMPACT FOR INDIA:
- Economic benefits:
- As Israel and the UAE work out a path to enhance bi-lateral trade the spill over could be a benefit for India especially as the two countries will be looking to build on the sectors of investment, tourism, direct flights, security, telecommunications, tech, energy, healthcare, culture and the environment.
- The peace deal actually benefits the Indian diaspora in the region given that in excess of 7 million Indians work across the GCC.
- Security aspects:
- New Delhi will play a much bigger in the regional security and stability in the GCC, given its closeness to Abu Dhabi and Tel Aviv
- The strategic partnership between the two nations also spills into the areas of counterterrorism, money laundering, cyber security, organised crime, human trafficking and anti-piracy.
- Increased possibility of interconnectedness
- Agreement opens the door to the first big re-approach between traditional adversaries in West Asia – Arabs and Israel. This will pave way for increased connectivity around the periphery – which includes India
INDIA’S CURRENT STAND ON ISRAEL-PALESTINE CONFLICT
- India was one of the few countries to oppose the UN’s partition plan in November 1947, echoing its own experience during independence a few months earlier. In the decades that followed, the Indian political leadership actively supported the Palestinian cause and withheld full diplomatic relations with Israel.
- India recognised Israel in 1950 but it is also the first non-Arab country to recognise Palestine Liberation Organisation (PLO) as the sole representative of the Palestinian. India is also one of the first countries to recognise the statehood of Palestine in 1988.
- In the 2014, India favored UNHRC’s resolution to probe Israel’s human rights violations in Gaza. Despite supporting probe, India abstained from voting against Israel in UNHRC IN 2015.
- In 2017, India voted against recognising Jerusalem as Israel’s capital in UN
- As a part of Link West Policy, India has de-hyphenated its relationship with Israel and Palestine in 2018 to treat both the countries mutually independent and exclusive.
- In June 2019, India voted in favour of a decision introduced by Israel in the UN Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) that objected to granting consultative status to a Palestinian non-governmental organization
- So far India has tried to maintain the image of its historical moral supporter for Palestinian self-determination, and at the same time to engage in the military, economic, and other strategic relations with Israel.
CONCLUSION:
- There is no doubt that Abraham Accord significantly impacts geopolitics in the Middle East, but to make it a step towards resolving Palestine issue, the international community must be able to press the Israel to relax its inhuman and illegal occupation of the Palestinian territories
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. Normalization of ties between UAE-Israel will have a direct bearing on India’s outreach into West Asia and the entire Middle East. Comment.

