MSME's Role in the Indian Economy
2022 JUL 8
Mains >
Economic Development > Indian Economy and issues > MSMEs
IN NEWS:
- June 27 is celebrated as the Micro-Small and Medium-sized Enterprises Day.
MORE ON NEWS:
- The UN General Assembly, in its 71st session on 6th April 2017, adopted 27th June as MSME Day to raise awareness of the massive contributions of MSMEs to the accomplishment of the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- According to the United Nations (UN), UMSMEs account for 90 per cent of businesses, 60 to 70 per cent of employment and 50 per cent of GDP worldwide.
- The World MSME Day this year is being observed under the theme of ‘Resilience and Rebuilding: MSMEs for Sustainable Development.
WHAT IS MSME?
- The MSME sector comprises micro, small and medium sized enterprises that are classified according to certain parameters.
- Revised Classification applicable w.e.f 1st July 2020:
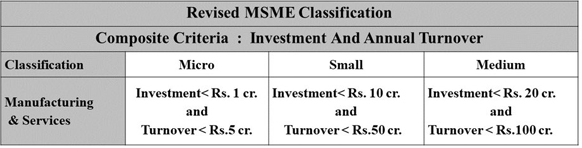
-
- Under the revised criterion, the combined factors of ‘Investment in plant and machinery’ and ‘Turnover’ are required to be considered to determine whether a business should be classified as a micro, small or a medium enterprise.
- In contrast, earlier the classification of an MSME unit was based only its investment in plant and machinery; and also depending on whether the enterprise was in the manufacturing sector or in the services sector.
- Earlier classification:
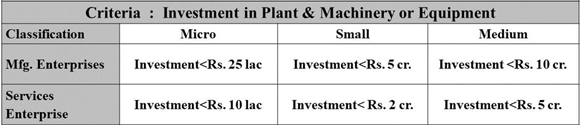
ROLE OF MSME IN INDIAN ECONOMY:
- Contribution to GDP:
- According to the MSME ministry data, there are about 6.3 crore MSMEs in India which contribute about 29% to the country's GDP from their national and international trade.
- MSMEs contribute around 6.11% of the manufacturing GDP and 24.63% of the GDP from service activities as well as 33.4% of India's manufacturing output.
- The MSME ministry has set a target to enhance its contribution to the GDP up to 50 percent by 2025 as India becomes a $5 trillion economy.
- Employment generation:
- MSMEs also play an important role in employment generation, as they employ about 110 million people across the country.
- It is the second largest employment generating sector after agriculture.
- Promote inclusive growth:
- MSMEs promote inclusive growth by providing employment opportunities in rural areas especially to people belonging to weaker sections of the society.
- For example, the coir industry employs about 7.37 lakh persons of whom majority are from rural areas belonging to the weaker sections of the society. Nearly 80% of the coir workers in the fibre extraction and spinning sectors are women.
- Inclusive and decentralized industrial development:
- MSMEs are complementary to large industries as ancillary units and this sector contributes significantly in the inclusive industrial development of the country.
- MSMEs' expansion, especially in rural areas, plays an imperative role in the economic expansion of the country and results in decentralised industrial development and better distribution of wealth and investment.
- Balanced regional development:
- MSMEs in rural areas controls the concentration of industry in urban areas by setting small scale units in remote areas, successful entrepreneurship development programmes can help in achieving balanced regional development.
- Promote innovation:
- It provides opportunity for budding entrepreneurs to build creativeproducts boosting business competition and fuels growth.
- Check on the migration of rural populations:
- Rural population moves towards urban for various reasons like income generation, searching good job, utilize various facilities etc.
- MSMEs will bring in or develop infrastructural facilities like roads, power, bridges etc.
- It reduces the gaps and disparities in income between rural and urban areas.
- All these factors can prevent the migration of people from rural to urban areas in search of jobs and better facilities.
- National self-reliance ( Atmanirbhar Bharat):
- MSMEs help to manufacture indigenous substitutes to imported products which reduce the dependence on foreign countries.
- There is also a possibility of exporting goods and services to earn foreign exchange for the country.
- Already MSME sector contributes around 45% of the overall exports from India.
- Hence, the import substitution and export promotion ensure economic independence and the country becomes self-reliance and it will support the government to achieve the objective of ‘Atmanirbhar Bharat’.
- Proper utilization of local resources:
- MSMEs in rural will help in the maximum utilization of local resources like raw materials and labour for productive purposes and thus increase productivity.
- Efficient and effective use of limited resources by the entrepreneurs leads to overall economic development of an area.
CHALLENGES AND PROBLEMS OF MSMEs:
- Lack of adequate and timely access to credit:
- Lack of adequate and timely access to finance continues to remain the biggest challenge for MSMEs
- 90% of the MSMEs are dependent on informal sources for funding
- Lack of sufficient collateral and high working capital needs.
- Lack of access to markets:
- Low outreach and non-availability of new markets.
- Lack of skilled manpower and ineffective marketing strategy.
- Difficult for MSMEs to sell products to government agencies.
- Competition from MNCs and other big industries.
- Technology is a big issue for MSMEs:
- Limited human resources and weak financial standing.
- MSMEs, particularly in the unorganised sector, show lower adaptability of new technology and innovation.
- Quality and export issues:
- Low quality products impact export competitiveness.
- Inadequate access to quality raw materials.
- Use of traditional machines causes low productivity.
- Regulatory hurdles:
- GST has emerged as the biggest compliance issue before the MSMEs.
- Cumbersome government procedures and rules for establishing new units.
- It takes 69 days to register a piece of property and costs about 8% of its value in India. To compare New Zealand gets this done in a single day.
- Bureaucratic delays in getting clearances.
- Poor litigation system in the country.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES:
- Udyami Mitra Portal:
- Launched by SIDBI to improve accessibility of credit and handholding services to MSMEs.
- MSME Sambandh:
- To monitor the implementation of the public procurement from MSMEs by Central Public Sector Enterprises.
- MSME Samadhaan -MSME Delayed Payment Portal
- Will empower Micro and Small entrepreneurs across the country to directly register their cases relating to delayed payments by Central Ministries/Departments/CPSEs/State Governments.
- Digital MSME Scheme:
- It involves usage of Cloud Computing where MSMEs use the internet to access common as well as tailor-made IT infrastructure.
- Prime Minister Employment Generation Programme :
- It is a credit linked subsidy program under Ministry of MSME.
- Revamped Scheme of Fund for Regeneration Of Traditional Industries (SFURTI):
- Organizes traditional industries and artisans into clusters and make them competitive by enhancing their marketability & equipping them with improved skills
- A Scheme for Promoting Innovation, Rural Industry & Entrepreneurship(ASPIRE):
- Creates new jobs & reduce unemployment, promotes entrepreneurship culture, facilitates innovative business solution etc.
- National Manufacturing Competitiveness Programme (NMCP):
- To develop global competitiveness among Indian MSMEs by improving their processes, designs, technology and market access.
- Micro & Small Enterprises Cluster Development Programme (MSE-CDP)- adopts cluster development approach for enhancing the productivity and competitiveness as wellas capacity building of MSMEs.
- Credit Linked Capital Subsidy Scheme (CLCSS) is operational for up gradation of technology for MSMEs.
- For extra reading on government initiatives: https://ilearncana.com/details/MSME-SECTOR-IN-INDIA/1452
WAY FORWARD:
- Adopt best practices:
- MSME need to adopt best practises and follow international standards to go forward for offering innovative solutions.
- Technology transfer and upgradation:
- Concerted efforts are needed to appraise MSMEs of new developments and technologies and how these can be usefully employed by them keeping in view the local conditions, in the language and mode which the locals can understand and assimilate.
- Focus should be on transfer of information and skill development to effectively use the transferred technology.
- MSMEs need a lot of handholding on several fronts:
- Clusters of MSMEs spread all across the country may be listed out and Common Facility Centers may be established at each MSME cluster, which, besides extending other common facilities like maintenance and provision of common facilities, facilitating availability of raw materials, marketing support, easy movement of goods and services etc., can guide and help in safeguarding the Intellectual Property Rights of the entities.
- These centres can facilitate individuals and entities in obtaining patents in respect of new technologies/products/innovations, in a cost-effective manner.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. “MSMEs plays a vital role in the economic development of India, particularly in the rural economy”. Elaborate?

