Migration & Brain Drain from India
2023 MAY 1
Mains >
Society > Globalisation > Employment
IN NEWS:
- Recently, the World Bank published the World Development Report, in which it highlighted that Indian workers see a 120% rise in their incomes outside India, while internal migration within India will only add about 40% to personal incomes.
- Also, another statistic from the OECD shows that nearly two-thirds of those migrating out of India seem to be highly educated, having received academic or vocational training.
- These findings highlight the "brain drain" from India due to migration.
WHAT IS "BRAIN DRAIN"?
- Brain drain occurs when educated, professional workers leave a country in order to move elsewhere where they can benefit from better pay, working conditions, lifestyle, and sometimes work-life balance.
REASONS FOR BRAIN DRAIN:
- Overseas university education:
- In primary education, India has made significant progress, but higher education remains a challenge. Even our stellar institutions like IIT and IIMs don’t make it to the list of the world’s top universities.
- Also, there is this growing sense of dissatisfaction generally, among the students that the current Indian education system is inept at preparing them for the challenges of an increasingly globalised world.
- The lack of innovative courses is drawing a lot of young students to leave Indian shores for better education overseas.
- For instance, several reports suggest that more than half of the first rankers in Class 10 and Class 12 examinations during 1996-2015 had migrated and were studying or employed overseas, mostly in the US.
- Low expenditure on research and Development (R&D):
- India’s gross domestic expenditure on research has stayed at 0.7% of the GDP for years. India has one of the lowest GERD/GDP ratios among the BRICS nations.
- So, students who are interested in R&D tend to migrate to other countries to continue their research.
- Lack of higher education opportunities in the country:
- The increasing cut-offs and legion of competitive exams make access to higher education difficult in India.
- Abroad, Indian students have an advantage over students from other countries in terms of skills and knowledge.
- The government also failed to provide a sufficient number of educational institutes as per the increasing population.
- Privatization of educational institutions and their higher tuition fees are also factors that force Indian students to migrate to other countries.
- For instance, the recent Ukraine-Russia conflict highlighted how medical students from India are getting a good education for lower fees in the post-Soviet countries.
- Lack of employment opportunities:
- Unemployment is more likely to be seen as a reason for India’s brain drain.
- According to the Center for Monitoring Indian Economy, unemployment in India rises with education. As of December 2021, one in five college graduates was unemployed.
- Indians have been leaving the country in droves because of job opportunities with better pay and work hours.
- For example, in the United States and the United Kingdom, professionals in the healthcare and science, technology, engineering, and math fields are in high demand.
- Better remuneration and standard of living:
- Better pay and living standards offered by the developed countries are one of the major reasons for the emigration of young professionals from India.
- Immigrant-friendly policies by developed countries:
- Due to the low population and shortage of skilled workers in the countries such as Australia, New Zealand, Germany, Japan, Italy, and other EU countries, Indians are now aiming to migrate to these countries.
- Many countries have improved their Immigration systems and streamlined their application process.
- For instance, Australia is one of those countries that opened its borders to migrants and students. The government is introducing more immigrant-friendly policies at three-level Immigration Structure – Federal, State, and Regional.
- Societal pressure:
- Indian youths are becoming more liberal and individualistic. However, Indian society as a whole has yet to accept this way of life.
- Hence, the pressure to live in a certain way in Indian society is curbing the freedom of choice of today’s youth, encouraging them to seek out western countries where the society is more liberal and non-interfering.
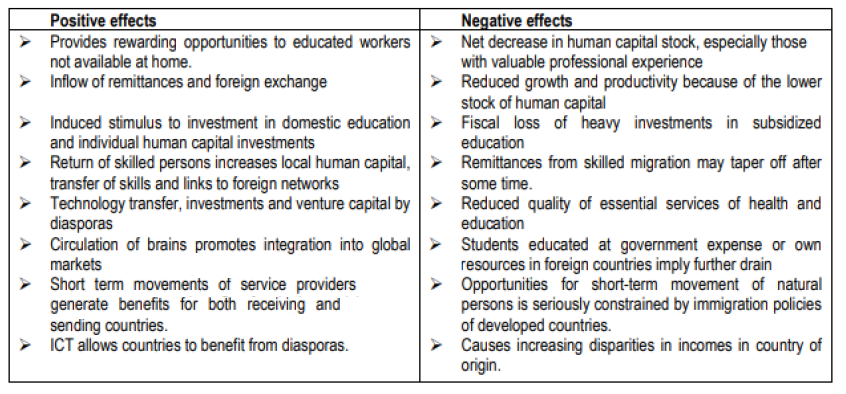
EFFECTS OF BRAIN DRAIN:
-------------------
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES TO TACKLE BRAIN DRAIN FROM INDIA:
- The Ramanujan Fellowship:
- Ramanujan Fellowship is meant for brilliant Indian scientists and engineers from outside India to take up scientific research positions in India, those Indian scientists/engineers who want to return to India from abroad.
- The Ramalingaswamy Fellowship:
- The idea behind starting Ramalingaswami Re-entry Fellowship in 2006-07 was to attract high quality Indian brains working abroad to pursue their research interests in life sciences, biotechnology and other related areas in India by providing them an attractive avenue to pursue their R&D interests in Indian institutions.
- Vaishvik Bharatiya Vaigyanik (VAIBHAV) summit:
- The VAIBHAV initiative aims to bring out the comprehensive roadmap to leverage the expertise and knowledge of global Indian researcher for solving emerging challenges. By bringing the Indian Overseas and Resident academicians/scientists together a structure of association will be evolved.
- Innovation in Science Pursuit for Inspired Research (INSPIRE):
- The basic objective of INSPIRE would be to communicate to the youth population of the country the excitements of creative pursuit of science and attract talent to the study of science at an early stage and build the required critical human resource pool for strengthening and expanding the Science & Technology system and R&D base.
WAY FORWARD:
- Create opportunities :
- The "young India" can contribute to the progress of the nation, but issues crop up when there is a dearth of opportunities.
- For instance, there can be various employment opportunities developed in the sectors of education, women empowerment, agriculture, handicrafts, etc., where highly skilled youth can contribute to the development and also earn a decent income through their contribution.
- More Indian companies in pharmaceuticals, electronics, ICT, etc should employ the recent graduate with lucrative packages, allowances, and decent working conditions. This helps in encouraging the youngsters to work in India itself and earn the benefit of their merit.
- Attract the non-resident Indians :
- The government should also be committed to not only retaining students who graduate from the country's premier educational institutions, but also to attracting non-resident Indians back to the country.
- Because opportunities in the field of technology that were previously unavailable in India, forcing non-resident Indians to seek employment elsewhere, are now becoming available in India.
- Taxation :
- There are a lot of reviews by economists who strongly believe that the taxation policy in India leaves much less scope for savings.
- Furthermore, there is still dissatisfaction with taxes not being used to solve various issues in the country.
- So, the taxation process should be simplified, and unnecessary burdens should be removed to create a favourable environment for professionals and thereby avoid brain drain.
- Work Culture:
- It is a known fact that most organizations in India do not work on strong principles and work culture. This leads to politics within an organization, communication gaps, absence of grievance redressal, etc leading to stress and anxiety in the employees.
- Many employees migrate to countries abroad with expectation of decent work atmosphere in lieu of staying with improper work culture.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. "Brain drain leads to reduced economic growth, limited innovative capacities, and a lack of skilled manpower." Discuss the causes and consequences of brain drain from India, as well as the steps being taken by the Indian government to halt it.
