Drug Trafficking: A Threat to National Security
2023 MAY 26
Mains >
Security > Border area management > Terrorism
IN NEWS:
- Recently, the Narcotics Control Bureau and the Indian Navy seized around 2,500 kg of methamphetamine from Indian waters off Kochi.
- The seized drugs are worth around Rs 15,000 crore in the market and, according to NCB officials, amount to the largest seizure by any Indian enforcement agency in terms of monetary value.
MORE ON NEWS:
- The seizure is part of Operation Samudragupt targeting maritime trafficking of drugs aimed at making the Indian Ocean region free of narcotics.
- It is also the first interception of a mother ship carrying drugs by an Indian agency, and a man suspected of Pakistani origin has been detained from the ship.
- The drugs had their origins in Pakistan and were loaded onto the mother ship from the Makran coast.
- Since the inception of Operation Samudragupt in January 2022, enforcement agencies have so far seized 3,200 kg of methamphetamine, 500 kg of heroin, and 529 kg of hashish.
WHY DRUG TRAFFICKING IS PREVALENT IN THE COUNTRY?
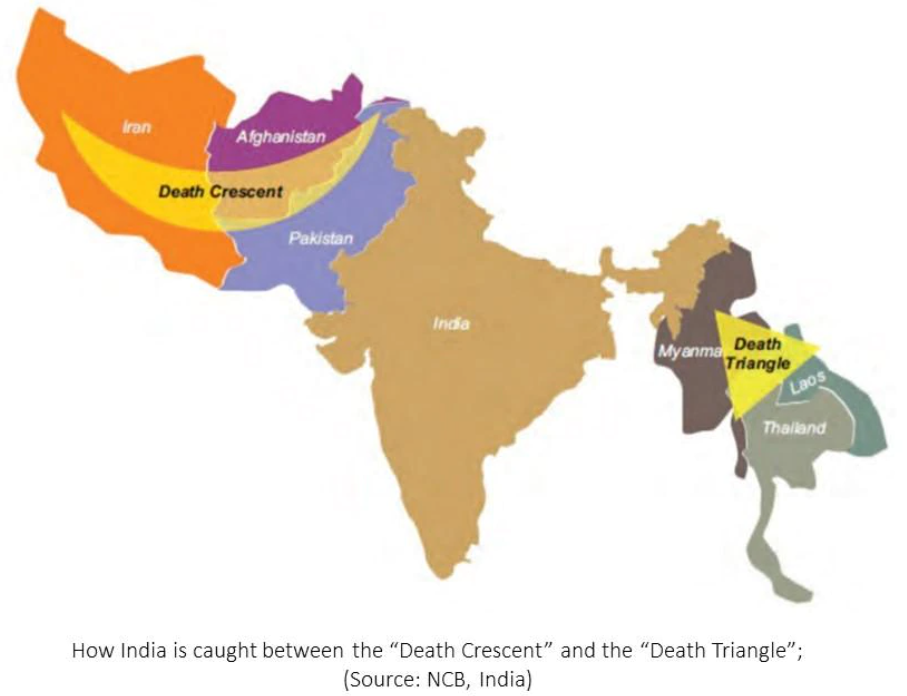
- Proximity to producing areas:
- India is sandwiched between the Golden Crescent and the Golden Triangle.
- This proximity has made India both a destination and a transit route for opiates produced in these regions.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
- Porous borders:
- India has porous borders with several countries that are known for drug production and trafficking.
- For instance, north-east India has porous and poorly guarded borders with Bangladesh, Nepal, and Myanmar, which are hotspots for drug smuggling.
- Ready availability within the country:
- Illicit cultivation of opium poppy still occurs in India.
- Also, India is a licit supplier of opium to the international pharmaceutical industry. However, despite strict controls, some portion of this product is diverted, which adds to the availability of drugs on the market.
- External state actors:
- Pak-backed crime syndicates and terrorist units thrive on cross-border narcotic trade.
- For instance, investigations have indicated the connection of drug traffickers from across borders with terrorist organisations like Lashkar-e-Toiba and Hizbul Mujahideen.
- New routes and modes of trafficking:
- The maritime route has become more active after the recent developments in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The use of drones to supply drugs and weapons across the border in Punjab is a new phenomenon.
- Darknet markets, cryptocurrency payments and doorstep deliveries are disrupting traditional drug markets because of their anonymity and low risks.
- Local support:
- For many in the rural and border regions of India, drug trade is a means to secure livelihood and escape poverty. Hence, smugglers often get support from locals.
- Legal loopholes:
- According to the present provisions of the NDPS Act, a seizure of less than five grams of heroin can lead to smaller imprisonment and fines. Moreover, the suspect can easily secure bail.
- In order to take advantage of the legal loopholes, most of the trafficking takes place in small quantities.
WHY DRUG TRAFFICKING IS A CHALLENGE TO NATIONAL SECURITY?
- Trafficking routes used for smuggling weapons and terrorists:
- The breach of the international borders of the country by drug traffickers means that the same routes could be used for smuggling in weapons as well as terrorists into the country.
- For instance, it has been found that the arms and explosives used in the 1993 serial bomb blasts in Mumbai were transported by the Dawood Ibrahim gang through traditional trafficking routes.
- Also, investigations into the Pathankot attack hinted that the terrorists entered India from Pakistan through the routes tried and tested by drug traffickers.
- Financing terrorist activities:
- The money generated by the illegal sale of drugs is used to finance terrorist activities.
- For instance, it is estimated that 15 percent of the finances of the J&K militants were generated through the sale of drugs. In the Northeast, while the smaller insurgent organisations are directly involved in drug trafficking to generate quick funds, the bigger insurgent organisations collect protection money from the drug peddlers in lieu of safe passage of drug consignments through their territory.
- Creates law and order problem:
- Large-scale availability and consumption of narcotics and drugs result in dysfunctional behaviour, thereby creating a law and order problem in society.
- Drug trafficking also has a direct bearing on the political process as drug cartels subvert, penetrate, and further corrupt state institutions to control the illegal drug trade.
- Darknet for illicit drug trafficking:
- Studies reveal that 62 percent of the darknet is being used for illicit drug trafficking.
- Cryptocurrency payments and doorstep deliveries through courier services have made darknet transactions attractive.
- Concerted and coordinated efforts by all the agencies will be required to tackle this growing threat. The success rate in catching traffickers using the darknet has been very low the world over.
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES:
- Operation Samudragupt:
- In February 2022 India began its fight against drug trafficking under Operation Samudragupta.
- This is a joint operation between the Indian Navy and the Narcotics Control Bureau (NCB).
- Operation Samudragupt is part of the Union government’s plan to make India drug-free by 2047.
- Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances (NDPS) Act, 1985:
- It defines the various narcotic drugs and psychotropic substances and lays out the prohibition, control and regulation of such substances
- The penalties under this Act are severe considering the consequences of drug abuse and its trafficking. All the offences under the NDPS Act are non-bailable.
- Narco-Coordination Centre (NCORD) under Ministry of Home Affairs
- It is tasked with combating drug trafficking and the use of illegal substances under the provisions of Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act.
- Narcotics Control Bureau:
- It was constituted in 1986 under the provisions of the NDPS Act.
- The NCB is a nodal agency that is responsible for coordination with various ministries, other offices & State/Central enforcement agencies with regard to drug law enforcement and also in respect of matters relating to drug abuse.
- It works under the Union Ministry of Home Affairs.
- International cooperation:
- For effective coordination with foreign countries, India has signed 37 Bilateral Agreements/Memoranda of Understanding.
- India is a party to the three United Nations drug conventions:
- Single Convention on Narcotic Drugs 1961,
- Convention on Psychotropic Substances, 1971
- Convention against Illicit Traffic in Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances, 1988.
- Technological efforts:
- Modern technological innovations such as Night Vision Devises, Hand-Held Thermal Imagers, Battle Field Surveillance Radars, Long Range Finders and High-Powered Telescopes are being used along the borders.
|
Four pillars and "Whole of the Government" approach:
- There are four pillars of the central government’s campaign to eliminate the menace of drugs from the country:
- Detection of drugs
- Destruction of Network
- Detention of culprits
- Rehabilitation of drugs abusers.
- Also, the government has adopted a "Whole of the Government" approach against drugs, in which all departments and agencies should move forward to make a drug-free India by increasing cooperation, coordination, and collaboration.
|
WAY FORWARD:
- There is a need to increase the focus on coastal security and sea routes, and tighter vigil should be maintained on the Southern Sea Route.
- It is also the need of the hour to strengthen the Anti-Narcotics Task Force constituted in various states so that decisive action could be taken in the fight against narcotics.
- The Ministry of Home Affairs is adopting the approach of 'Bottom to Top' and 'Top to Bottom' in the matters of drugs, other States and institutions should also adopt the same approach to completely eliminate the menace of drugs.
- As the Home Minister said, the problem of drug trafficking is not related to a state or the Centre alone but is a national problem, and the efforts to deal with it should also be national and unified. He said that the fight against drugs is to be fought not only by the government but also by the people.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. "The narcotics trade is assuming dangerous proportions all over the world, and India is no exception". Discuss why drug trafficking is a serious national security issue.
