Military Logistics Agreements
2021 DEC 3
Mains >
International relations > Agreements > DEFENCE AGREEMENTS
WHY IN NEWS?
- India is all set to conclude the bilateral logistics agreement with Russia soon while the agreement with the U.K. is in the final stages of conclusion
WHAT ARE MILITARY LOGISTICS AGREEMENTS?
- Military logistics agreements are merely administrative arrangements between strategic partners that would facilitate replenishment of fuel, rations, and spare parts, as well as berthing and maintenance for each other’s warships, military aircraft, and troops during port visits and joint exercises, on a reciprocal basis, essentially simplifying the process of extending logistical support to one other.
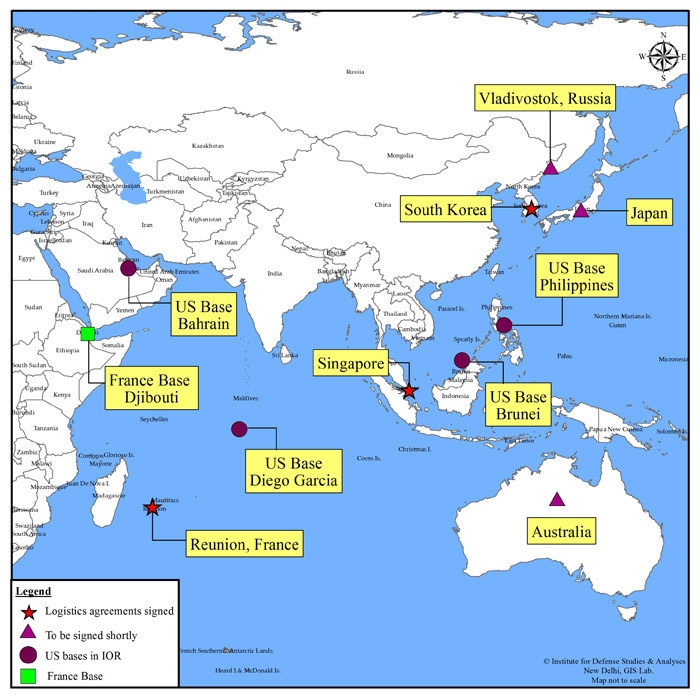
- India has signed several logistics agreements with all Quad countries (U.S, Japan, Australia), France, Singapore and South Korea beginning with the Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement (LEMOA) with the U.S. in 2016.
LOGISTICS SUPPLY AGREEMENT SIGNED BETWEEN INDIA AND OTHER COUNTRIES
- India and USA:
- India has now signed all four foundational agreements with the US.
- LEMOA in 2016:
- It stands for Logistics Exchange Memorandum of Agreement
- This agreement allows the use of each other’s military’s logistics facilities.
- LEMOA will increase the range and reach capability of the Indian Navy world over.
- For example, Indian Navy can use a US base located in Guam, Djibouti, Diego Garcia etc. thus increasing the reach of Indian Navy.
- COMCASA in 2018:
- COMCASA stands for Communications Compatibility and Security Agreement
- It mainly focuses on using encrypted communication networks, which is required for optimum utilization of high-end defence equipment like P-8I Maritime Surveillance aircrafts which is currently used by Indian Navy.
- BECA in 2020
- It stands for Basic Exchange and Cooperation Agreement for Geo-Spatial cooperation (BECA)
- With this agreement Indian military can access the geo-spatial intelligence data from the United States of America (USA). This will help in increasing the accuracy of long range weapons.
- While the General Security of Military Information Agreement (GSOMIA) was signed a long time ago, an extension to it, the Industrial Security Annex (ISA), was signed in 2019.
- India and France:
- The logistics supply agreement between India and France will promote peace and stability in Pacific and Indian Ocean region.
- The Navies of India and France, will share maritime intelligence.
- India and Australia
- India and Australia signed a comprehensive Mutual Logistic Support Agreement (MLSA) in 2020.
- Both nations emphasised on a shared vision for maritime cooperation in the Indo-Pacific.
- India and Japan
- India and Japan signed a logistics supply agreement known as Acquisition and Cross-Servicing Agreement (ACSA) in 2020.
- India and Singapore
- Logistics support agreement signed between India and Singapore in 2020, encompasses the ship-borne helicopters, aircrafts, warships, and submarines.
- India and South Korea
- With this agreement, Indian Navy’s reach has extended all the way to the North of South China Sea.
- India and Russia
- The India-Russia bilateral logistics agreement is called the Reciprocal Exchange of Logistics Agreement (RELOS)
- It gives India access to Russian facilities in the Arctic region which is seeing increased global activity as new shipping routes open up and India’s own investments in the Russian Far East.
NEED FOR SUCH AGREEMENT:
- Threat from China:
- China’s increasing activities in the Indo-Pacific have motivated India to embrace military logistics agreements with a wide variety of partners.
- This included the development of islands in the South China Sea, constant forays of Chinese warships into the Indian Ocean and acquisition of a military base at Djibouti in 2017.
- China’s increasing economic and military heft thus required an effective counterbalance.
- Enhance India’s image as a ‘net security provider’ in Indian Ocean:
- These agreements feed into the Indian Navy’s requirement to maintain round-the-clock and round-the-year presence in its primary areas of interest, the Indian Ocean Region (IOR) and, going forward, the Indo-Pacific.
- To increase operational capability of Indian navy:
- Prior to these agreements, the mission-deployed Indian warships were constrained to periodically replenish their fuel and logistics supplies from either an Indian naval fleet tanker deployed in the area or by entering the nearest Indian or foreign port.
- With the signing of these agreements, Indian warships have been able to extend their ‘sea-legs’ on station by taking fuel from naval fleet tankers of partner countries deployed in the region or by entering their ports.
- For instance, since the signing of LEMOA with the US in 2016, Indian warships deployed near the Gulf of Aden have been fuelling from the US Navy tankers in the region
ADVANTAGES
- Expanding India’s military reach:
- These agreements expands India’s military reach, especially maritime outreach and influence in various regions that are strategically important to India
- For example:
- RELOS gives India access to Russian facilities in the Arctic region.
- LEMOA provides India refueling facilities and access to U.S. military facilities in Djibouti, Diego Garcia, Guam, and Subic Bay.
- Agreement with France extends New Delhi’s reach into the southwestern Indian Ocean region, where the French have a military presence, and thus access to the Reunion Islands near Madagascar and Djibouti
- Saves time and cost:
- These agreements simplify the bookkeeping during events like bilateral military exercises, humanitarian assistance and ensure that the forces of the visiting countries are benefitted by using the host nation’s existing logistics network, which additionally reduces overall costs and saves on time.
- Enhanced cooperation and greater inter-operability between nations
- As these agreements ensures reciprocal facilitation of forces when engaged in activities such as disaster relief, humanitarian aid, peacekeeping operations and support to each other’s forces during joint deployment under an international mandate of the United Nations (UN).
- Strategic importance:
- It permits a country to project power away from its borders in international waters.
- This extends the strategic reach and footprint of the country in far off waters and enhances its sustainability therein manifold.
- Improves training capabilities of military:
- As logistics agreements between countries supports to conduct training in each other’s areas.
- Enhance morale of military personnel:
- Logistics agreements also includes rest and recuperation of crew members, supply of essential items like water, foods etc >> hence increased amenities for troops.
- Increasing the Maritime Domain Awareness:
- Logistics agreement helps in swift response to a crisis situation, tracking of enemy ships, thereby increasing the Maritime Domain Awareness (MDA).
- Helps in power projection:
- Logistics agreements help India in power projection in international waters, far away from its borders.
- Divests the need for a nation to invest in overseas bases
- Development of overseas bases will incur installation, maintenance and manpower costs.
- A logistics agreement provides for expanding a nation’s operational footprint and diversifying its international presence at the same time at a much lesser cost than developing of overseas bases.
CONCERNS
- Compromise strategic autonomy
- For example signing of logistics supply agreement with U.S will results in visits by U.S inspectors to Indian bases, intrusive access to U.S in Indian military communication systems
- Reorientation of foreign policy:
- Indian foreign and military policy will have to reorient itself to likes and dislikes of partner country.
- This can strain traditional friendships with other nations in the region.
- For example, signing of LEMOA with U.S might strain traditional friendships with Russia.
- Issue of jurisdiction:
- The question of under which jurisdiction does the illegal behaviour of partner nations troops falls remains unaddressed.
- Burdensome procedure for Indian military
CONCLUSION
- India must effectively utilize its military logistics agreements with other countries to combat China’s growing role in Asia and Indo-Pacific and ensure free, open and rules-based order in the region.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. In context of aggressive behaviour of China in Indo-Pacific, analyse the relevance of India’s military logistics agreements with partner nations?
