Sea Mounts
2023 APR 29
Preliminary >
Geography > Oceanography > Oceanography
Why in news?
- Recently, in an astonishing discovery, scientists have reported finding 19,325 new seamounts after poring through new high-resolution data. This is an addition to already mapped 24,000 seamounts across the world’s oceans.
About Sea Mounts:
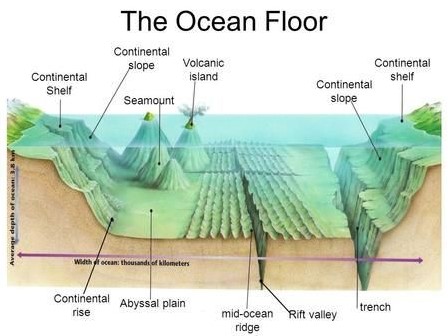
- A seamount is an underwater mountain.
- Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to 1,000–4,000 m in height.
- A seamount is technically defined as an isolated rise in elevation of 1,000 m or more from the surrounding seafloor, and with a limited summit area, of conical form.
Formation:
- They are formed through volcanic activity and scientists recognise them as hotspots for marine life.
- Like volcanoes on land, seamounts can be active, extinct or dormant volcanoes.
Area of formation:
- Most seamounts are formed near mid-ocean ridges, where the earth’s tectonic plates are moving apart, allowing molten rock to rise to the seafloor.
- The planet’s two most-studied mid-ocean ridges are:
- The Mid-Atlantic Ridge and the East Pacific Rise.
- Some seamounts have also been found near intra plate hotspots – regions of heavy volcanic activity within a plate – and oceanic island chains with volcanic and seismic activity called island arcs.
Role and Importance of Seamounts:
- Information on evolution of Tectonic Plates:
- Because seamounts are formed when molten rock comes up from below the tectonic plates, they provide information about the mantle’s composition and about how tectonic plates evolve.
- Water Circulation:
- Oceanographers also study seamounts to understand their influence on how water circulates and absorbs heat and carbon dioxide.
- Home to diverse biological communities:
- Seamounts are home to diverse biological communities. They are good places for life because they can cause localised ocean upwelling – the process by which nutrient-rich water from deep within the ocean moves up to the surface.
- Insights on Evolution of Earth:
- Forged and altered by volcanic and tectonic processes that are intimately linked to the deep earth. They give us insights into the forces that have shaped the face of our planet.
- Mineral Harvesting:
- They are also being targeted by mining companies that hope to harvest the minerals that often collect around seamounts as a result of hydrothermal activity.
- Hotspot of marine life:
- Seamounts also attract an abundance of marine life and are productive fishing grounds more than 80 commercial species worldwide.
PRACTICE QUESTION
Consider the following statements:
1. Most seamounts are formed near mid-ocean ridges
2. Seamounts are helpful in studying mantle’s composition
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
