AIIB & ADB
2021 OCT 29
Mains >
International relations > International Institutions > Development Banks

ADB & AIIB
IN NEWS:
- The Government of India has applied for a USD 2 billion loan from the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) to procure as many as 667 million doses of COVID-19 vaccines.
I. ASIAN DEVELOPMENT BANK:
- ADB was conceived in 1966 as a financial institution that would be Asian in character and foster economic growth and cooperation in the region.
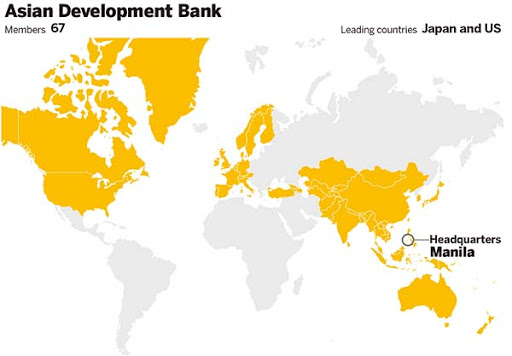
- It is modeled based on the World Bank and is headquartered in Manila, Philippines.
- It admits members of the United Nations Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific (UNESCAP).
OBJECTIVE:
- The main objectives of ADB are to reduce poverty and foster economic growth and cooperation in the region of Asia and Far East.
- The Bank aims at achieving this broad objective through the following functions:
- Mobilization and promotion of investment of private and public capital for productive purposes.
- Utilization of its resources for financing those development projects which contribute most to the harmonious economic growth of the region
- Coordination of plans and policies of the member countries.
- Provision of technical assistance to the member countries.
- Cooperation with the UN and other international organizations.
STRUCTURE:
- The highest decision-making tier at ADB is its Board of Governors, to which each of ADB’s 67 members nominate one Governor and an Alternate Governor to represent them. The Board of Governors meets formally once a year at an Annual Meeting held in a member country.
- The Governors elect 12 members to form the Board of Directors, which performs its duties full time at the ADB headquarters. The Directors supervise ADB's financial statements, approve its administrative budget, and review and approve all policy documents and all loan, equity, and technical assistance operations.
- The ADB President, under the Board’s direction, conducts the business of ADB. The President is elected by the Board of Governors for a term of five years and may be re-elected.
- The ADB has a weighted voting system similar to the World Bank, where votes are distributed in proportion with members’ capital subscriptions.
- Japan holds the largest proportion of shares at 15.7%. The United States holds 15.6%, China holds 6.5%, India holds 6.4%, and Australia holds 5.8%.
LENDING OPERATIONS:
- The ADB lending operations are broadly of two types: ordinary and specialized operations.
- The lending operations financed out of the ordinary capital resources of the Bank are called as ordinary operations.
- The specialized operations of the Bank are financed from the various Special Funds such as the Technical Assistance Special Fund, Asian Development Fund, and Agricultural Special Fund.
- Apart from providing direct loans for projects in member countries, the Bank also provides indirect loans to the financial institutions in the member countries.
- The ADB has recently established the ‘Asia-Pacific Vaccine Access Facility (APVAX)’ to provide a resource envelope and support mechanism to developing member countries as they procure and deliver COVID-19 vaccines safely and effectively.
INDIA AND ADB:
- India has been a member of ADB since its inception in 1966. India is now the bank’s fourth-largest shareholder and top borrower.
- ADB commenced operations in India in 1986 and has committed 252 sovereign loans totaling USD 45.85 billion for India since then.
- ADB support is being utilized in areas such as infrastructure and services in transport, energy, urban development, agriculture and natural resources, finance, and education and training.
- Eg: ADB has committed USD 500 million to build the high-speed 82-kilometer Delhi-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System corridor.
CRITICISM OVER ADB:
- Emphasis on lending to private sector projects:
- The ADB operations indicate that higher priority has been given to the private sector projects. It has taken very little interest in the development of public sector which has a key role in the development process of LDCs.
- Tied loans:
- The ADB generally provides tied loans and the borrowing countries are required to utilise funds only for the specified purpose. Such a restriction tends to discourage the developing countries who are in greater need of non-project investible resources.
- Insensitive to the poor:
- On several occasions, the ADB has been criticised for funding projects that had detrimental outcomes for poor and marginalized communities.
- High rate of interest:
- The interest rate charged by the ADB on credits is relatively higher than that charged by some other international financial institutions. The proportion of concessional loans in the total lending of the ADB has remained low.
- US-Japan dominated:
- Japan and the United States are the largest contributors and therefore have the largest voting share. Due to this excessive power, the two have had extensive influence over lending, policy and staffing decisions.
- Political bias in Lending:
- There is a serious charge against the credit operations of the ADB that there is an element of political bias in its loan policy. The ADB seems to promote the strategies and interests of the United States and her allies.
II. ASIAN INFRASTRUCTURE INVESTMENT BANK (AIIB):
- The Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank (AIIB) is a multilateral development bank with a mission to improve social and economic outcomes in Asia.
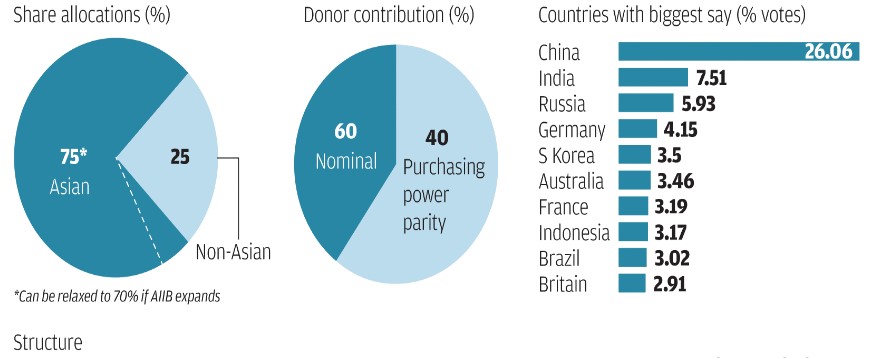
- The bank was proposed by China in 2013. It is established by the AIIB Articles of Agreement with 57 founding members. It began operations in January 2016 and is headquartered in Beijing.
- Membership is open to all members of the World Bank or the Asian Development Bank and is divided into regional and non-regional members. Currently it has 103 approved Members.
Note: America and Japan have been the largest contributors to the ADB but have both chosen not to apply for AIIB membership. On the other hand, Russia is a founding regional member of AIIB, its third-largest contributor and not an ADB member.
- The purpose of the bank is to:
- Foster sustainable economic development, create wealth and improve infrastructure connectivity in Asia by investing in infrastructure and other productive sectors
- Promote regional cooperation and partnership in addressing development challenges by working in close collaboration with other multilateral and bilateral development institutions.
FUNCTIONS:
- Promote investment in the region of public and private capital for development purposes, in particular for infrastructure and other productive sectors.
- Utilize the resources at its disposal for financing such development, including those projects and programs which will contribute most effectively to the harmonious economic growth of the region.
- Encourage private investment in projects, enterprises and activities contributing to economic development in the region.
AIIB’S GOVERNING BODIES
The bank follows a three-level governance:
- Board of Governors:
- It is the Bank’s highest authority, composed of one Governor appointed by each member, meeting annually.
- All powers of the Bank are vested in the Board of Governors
- Board of Directors:
- It is responsible for the direction of the general operations of the Bank.
- It is composed of 12 Directors elected by one or more Governors representing particular members, meeting at least quarterly. Nine Directors are regional and three Directors are non-regional.
- The President:
- He/she is elected by the Board of Governors, through an open, transparent and merit-based selection process.
- He/she conducts the day to day business of the Bank, under the direction of the Board of Directors.
DECISION MAKING PROCESS:
- AIIB follows the practice of weighted voting, rather than equal votes for each member. The total voting power of each AIIB member consists of the sum of its share votes, basic votes and, in the case of a Founding Member, its Founding Member votes.
- Share votes. Share votes are equal to one vote for each share of stock held by a member. Larger shareholders consequently hold more share votes.
- Basic votes are the same for each member
- Founding Member votes are assigned to those Signatories who become Founding Members by completing membership requirements before the deadline set in the AIIB Charter. They are fixed at 600 votes per member.
INDIA AND AIIB:
- India is the second shareholder of the bank and also one of the biggest prospective markets for transport infrastructure development among AIIB’s Asian members.
- India is the top borrower from the China-led and China-created multilateral development bank.
- So far, AIIB has invested in 21 projects in India, amounting to almost USD 5.5 billion. Another 20-30 projects are in the pipeline amounting to another USD 5 billion, which will be financed in next two years.
- Some of the major AIIB funded projects in India are the Mumbai urban transport project, solar projects in Rajasthan, irrigation and flood management project in West Bengal and investments in the National Infrastructure Investment Fund (NIIF).
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. ‘India stands to gain from the competition between AIIB and Asian Development Bank’. Discuss?


