Flash Floods
2023 AUG 3
Mains >
Disaster Management > Disasters > Floods
IN NEWS:
- The monsoon season in India this year has been accompanied by flash floods in different parts of the country, including Himachal Pradesh.
WHAT ARE FLASH FLOODS?
- Flash floods are sudden and rapid floods that occur within a short period of time, typically within hours of heavy rainfall or rapid snowmelt caused by sudden increases in temperature or rain on snow, or after a sudden release of water from a dam or levee failure etc.
- They usually cover a relatively small area and occur with little to no notice.
- They are characterised by swift and powerful flows of water that can quickly inundate low-lying areas, such as riverbeds, canyons, and urban areas with poor drainage systems.
- The US’s meteorological agency, the National Weather Service, says flash floods are caused when rainfall creates flooding in less than 6 hours.
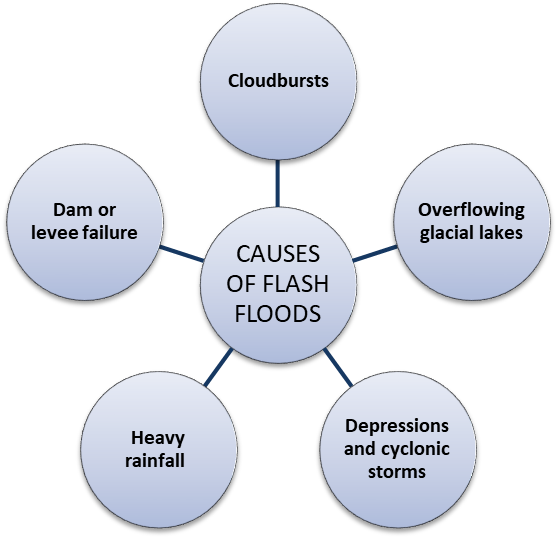
INDIA'S VULNERABILITY TO FLASH FLOODS:
- According to government data from a project by the Assam State Disaster Management Authority, India is the second-worst flood-affected country in the world after Bangladesh and accounts for one-fifth of the global death count due to floods.
- In India, flash floods are often associated with cloudbursts (sudden, intense rainfall in a short period of time). Himalayan states further face the challenge of overflowing glacial lakes, formed due to the melting of glaciers, and their numbers have been increasing in the last few years.
- Also, depressions and cyclonic storms in the coastal areas of Orissa, West Bengal, and Andhra Pradesh cause flash floods.
- The National Disaster Management Authority (NDMA) states that one of the reasons for flood situations occurring so frequently is that nearly 75 percent of the total Indian rainfall is concentrated over a short monsoon season of four months (June to September). As a result, the rivers witness heavy discharge during these months.
- Flash floods have been commonly witnessed in cities like Chennai and Mumbai. They occur in urban areas located near small rivers since hard surfaces such as roads and concrete do not allow the water to absorb into the ground.
RISKS OR CONCERNS ASSOCIATED WITH FLASH FLOODS:
- Occur without warning:
- The very nature of flash floods makes them fast and very difficult to predict. Since they can occur without warning, the casualty and death toll would be higher.
- More structural damage and loss of critical infrastructure:
- Flash floods, along with the huge force of water, cause movements of rock, boulders, earth, or debris down the slope as they are accompanied by landslides.
- Thus, flash floods can cause more structural and infrastructure damage than normal floods.
- Large debris and floodwaters from flash floods can cause structural damage to bridges and roadways, making travel impossible. Power, telephone, and cable lines can also be taken out by flash floods. Flood waters can disrupt or contaminate groundwater, making tap water unfit for consumption.
- Impacts on the environment:
- The environment also suffers when flash floods occur.
- For instance, flash floods carry with them a large amount of sand, silt, and other debris as they travel and deposit a thick layer of it in the lowlands above, which may cause destruction to the flora and fauna in the region. Thus, flash floods can destroy the natural balance of the ecosystem.
HOW TO PREPARE FOR AND MANAGE FLASH FLOODS?
- Proper monitoring and early warning systems:
- Early warning systems, such as weather forecasts and monitoring of river levels and the movement of glaciers, in case of mountainous regions, are key to mitigating the risks associated with flash floods.
- For instance, the India Meteorological Department (IMD) issues warnings for regions that may be at risk for flash floods. Also, the integrated flood warning system (IFLOWS) in Mumbai and the intelligent flood warning system’ in Chennai could be helpful for effective monitoring and warning in cases of urban flash floods.
- Local cooperation and participation:
- Flash floods are localised hazards, so local cooperation and participation efforts are essential to reducing risk.
- The effectiveness of vulnerability reduction relies on the awareness and preparedness of the inhabitants of the flood plain. Through a participatory approach, the local populations can have opportunities to learn about the risks and realise their respective responsibilities for risk reduction.
- Flash flood hazard mapping and spatial planning:
- Spatial planning can be an effective means of limiting the increase in flash flood exposures by limiting the flood damage potential.
- The key is to take into account information about flash flood hazard areas in spatial planning. It is important that a flash flood hazard map be considered in spatial management plans.
- Also, land-use regulation that controls new construction in regions of high flood risk and introduces necessary restrictions in regions of medium and low risk is required.
- Measures in urban areas:
- Developing proper urban drainage systems, cleaning and unblocking drains, and adopting appropriate rainwater management practices .
- Promote and build rainwater harvesting mechanisms so more and more rainwater can be stored and put to good use instead of causing flash floods.
- Also, parks, gardens and rooftop gardens help absorb the rainwater and prevent flash flooding.
CONCLUSION:
- To deal with the current situation of repeated flash floods, a comprehensive strategy of monitoring river levels, weather patterns, glaciers in mountain areas, etc., planning development in a way that is sensitive to the region’s ecology, and mitigation to reduce the extent of damages is needed.
- For extra reading on floods :
|
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. "Flash floods are characterised by a short response time and have the potential to severely impact and damage communities". Discuss India's vulnerability to flash floods and suggest measures for the preparedness and management of flash floods.
