Presidential Election in India
2022 MAR 26
Preliminary >
Polity > Executive > President
Why in news?
- Incumbent Ram Nath Kovind will retire in July and his successor will be elected through an indirect election. According to convention, the election for the office of the President of India is notified in mid-June and polling begins in July.
How is President elected?
- Article 54 states that:
- The President of India is elected indirectly by the single-transferable voting system.
- The President is elected by an electoral college consisting of elected members of state legislative assemblies and Parliament.
- The nominated members of Parliament and state legislatures are not allowed to vote in the presidential election.
- Hence the electoral college of the presidential election consists of:
- Elected members of Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha
- Elected members of Legislative Assemblies of the states
- Elected members of Legislative Assemblies of the Union Territories of Delhi, Jammu & Kashmir and Puducherry.
- Where an assembly is dissolved, the members cease to be qualified to vote in presidential election, even if fresh elections to the dissolved assembly are not held before the presidential election.
- Article 55 states the manner of the election of the President. It states that:
- The president is elected indirectly by an electoral college.
- The election shall be done by a secret ballot.
- The election shall be held in accordance with the system of proportional representation by means of a single transferable vote.
Value of Vote of MP and MLA in President Election in India
- The number and value of votes are based on the population in 1971 rather than the current population, as a result of the 42nd Amendment, and extended by the 84th Amendment, with the intention to encourage family planning programs in the states by ensuring that states are not penalised for lowering their population growth.
- The value of votes cast by elected members of the state legislative assemblies and both houses of parliament are determined by the provisions of article 55(2) of the Constitution of India.
- The formula for determining the number of votes held by an MLA is:
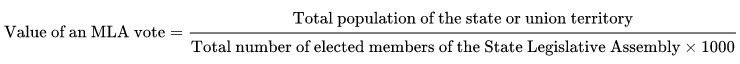 ???????
???????
- Hence value of votes for each MLAs varies from state to state
- For example: Value of votes for each MLAs in Andhra Pradesh, Goa, Kerala and UP is 159, 20, 152 and 208 respectively.
- The value of an MP's vote is calculated by dividing the total value of all MLAs' votes by the number of MPs. The formula for determining the number of votes held by an MP is:

Process of Election
- Nomination
- The nomination of a candidate for election to the office of the president must be subscribed by at least 50 electors as proposers and 50 electors as seconders.
- Each candidate has to make a security deposit of Rs. 15,000 in the Reserve Bank of India
- The security deposit is liable to be forfeited in case the candidate fails to secure one-sixth of the votes polled.
- Process:
- System of proportional representation by means of the single transferable vote ensures that the successful candidate is returned by the absolute majority of votes.
- A candidate, in order to be declared elected to the office of President, must secure a fixed quota of votes.
- The quota of votes is determined by dividing the total number of valid votes polled by the number of candidates to be elected (here only one candidate is to be elected as President) plus one and adding one to the quotient.
- Each member of the electoral college is given only one ballot paper. The voter, while casting his vote, is required to indicate his preferences by marking 1, 2, 3, 4, etc. against the names of candidates.
- This means that the voter can indicate as many preferences as there are candidates in the fray.
- In the first phase, the first preference votes are counted.
- In case a candidate secures the required quota in this phase, he is declared elected.
- Otherwise, the process of transfer of votes is set in motion. The ballots of the candidate securing the least number of first preference votes are cancelled and his second preference votes are transferred to the first preference votes of other candidates. This process continues till a candidate secures the required quota.
Disputes:
- All doubts and disputes in connection with election of the President are inquired into and decided by the Supreme Court whose decision is final.
- The election of a person as President cannot be challenged on the ground that the electoral college was incomplete (ie, existence of any vacancy among the members of electoral college).
Eligibility to hold the office of President of India
- He should be a citizen of India.
- He should have completed 35 years of age.
- He should be qualified for election as a member of the Lok Sabha.
- He should not hold any office of profit under the Union government or any state government or any local authority or any other public authority
Term of President’s Office
- The President holds office for a term of five years from the date on which he enters upon his office.
- However, he can resign from his office at any time by addressing the resignation letter to the Vice-President.
- Further, he can also be removed from the office before completion of his term by the process of impeachment.
- The President can hold office beyond his term of five years until his successor assumes charge.
- He is also eligible for re-election to that office. He may be elected for any number of terms6. However, in USA, a person cannot be elected to the office of the President more than twice.???????
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Consider the following statements:
1. President of India is not eligible for re-election to that office
2. Doubts and disputes in connection with election of the President are inquired into and decided by the Supreme Court
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Answer
 ???????
???????