Sea Butterflies
2023 MAY 18
Preliminary >
Environment and Ecology > Biodiversity > Species in news
Why in news?
- The population of the sea butterflies in the Southern Ocean is shrinking due to climate change, making them extremely vulnerable.
About Sea Butterflies:
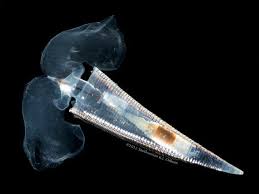
- Sea butterflies are a suborder of sea snails known as shelled pteropods.
- They have muscular feet that allow them to swim in water instead of gliding on solid surfaces.
- Sea butterflies are holoplanktonic (organisms that pass their whole life floating, drifting, or swimming weakly in the water) and spend their entire life cycle in the water column.
- They have a reduced or absent gill and rely on their body surface for gas exchange
- They are found in all oceans but are more diverse and abundant in colder waters.
Importance:
- They are a major food source for many fish, seabirds, whales, and other marine animals.
- They also play a key role in transporting carbon from the surface to the deep ocean through their shells and fecal pellets.
Climate Change Impact on Sea Butterflies:
- Impact of rising ocean temperatures due to climate change:
- Changes in distribution and abundance of sea butterflies.
- Seek optimal thermal conditions for development and survival.
- Alters food availability and quality.
- Impacts ocean currents and mixing affecting sea butterfly transport.
- Impact of ocean acidification:
- Reduced availability of carbonate ions necessary for shell formation and maintenance.
- The ocean is the most acidic in winter because cooler water absorbs more CO2. This means, the winter months are the most dangerous for the shelled sea butterflies.
- Their shell is mostly transparent and very fragile and can be easily dissolved by ocean acidification.
Sea butterflies and Impact Antarctic Marine Ecosystems:
- Decreasing the carbon sequestration capacity of the ocean:
- Sea butterflies contribute to the "biological pump," transporting carbon from the surface to the deep ocean through their shells and fecal pellets.
- Population decline reduces the amount of carbon sequestered (process of capturing and storing atmospheric carbon dioxide) in the ocean.
- This results in increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere and further ocean acidification.
- Disrupting the balance of the marine food web:
- Sea butterflies play a crucial role in linking primary producers (phytoplankton) with secondary consumers (zooplankton) and higher trophic levels.
- Decline in sea butterfly population can alter the structure and function of the marine food web.
- Biodiversity and productivity of the Antarctic marine ecosystem may be affected.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
With reference to ‘Sea Butterflies’, consider the following statements:
1. They cannot survive in colder waters
2. They have a reduced or absent gill and rely on their body surface for gas exchange
3. Decline in population of Sea Butterflies increases carbon dioxide in the atmosphere
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Answer
