5G Services In India
2022 APR 13
Mains >
Science and Technology > Communication technology > infrastructure
IN NEWS:
- Recently, the Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI) has recommended 36% reduction in base price of 5G spectrum.
- The government aims to conduct spectrum auctions in 2022 in order to enable roll out of 5G services by private players before March 2023.
WHAT IS 5G?
- 5G or fifth generation is the latest cellular communication standard for transmitting data over wireless networks. The "G" stands for "GENERATION".

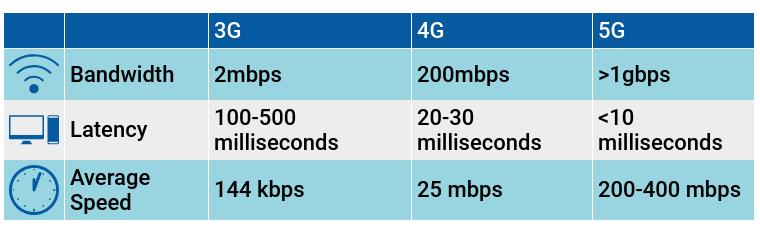
- Each Generation is defined as a set of telephone network standards for the technological implementation of a particular mobile phone system. With each generation the speed and the data capacity increases and the technology used to achieve that speed changes. For eg, 1G offers 2.4 kbps, 2G offers 64 Kbps , 3G offers 144 kbps-2 mbps whereas 4G offers 100 Mbps - 1 Gbps.
- 5G mainly works in 3 bands, namely low, mid and high frequency spectrum
- The low band spectrum has shown great promise in terms of coverage and speed of internet and data exchange but the maximum speed is limited to 100 Mbps.
- This band suits commercial cellphone users who may not have specific demands for very high speed internet.
- The mid-band spectrum offers higher speeds compared to the low band, but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals.
- This band can be utilised by industries and specialised factory units for building captive networks that can be moulded into the needs of that particular industry.
- The high-band spectrum offers the highest speed of all the three bands, but has extremely limited coverage and signal penetration strength.
- Internet speeds in the high-band spectrum of 5G has been tested to be as high as 20 Gbps (the maximum internet data speed in 4G has been recorded at 1 Gbps).This band has application in several cutting edge technologies like IoT(Internet of Things).
OPPORTUNITIES WITH 5G:
INITIATIVES BY GOVERNMENT
- National Digital Communications Policy 2018
- Policy lays out objectives with respect to emerging digital technologies, including 5G, AI, IoT, Cloud and Big Data.
- Constituted a high-level forum on 5G.
- Centre launched a project 'Building an End-to-End 5G Test Bed' to advance innovation and research in 5G.
CHALLENGES/CONCERNS IN REALIZING 5G IN INDIA:
- Spectrum availability: Department of telecommunications (DoT) has earmarked 300 MHz in the mid-band spectrum of the 3.3-3.6 GHz range for 5G. It is argued that this 300 MHz is not enough for a large country like India. Also, the defence department and ISRO have sought 125MHz out of this 300MHz, which leaves just 175MHz for commercial telecom services.
- Spectrum pricing: Although the reduction in base price recommended by TRAI is largely on expected lines, it is lower than the industry’s demand. Indian telecom sector is already suffering from debt crisis which prevents them from making investments for infrastructure expansion. It won’t be viable for them to shift to 5G with this pricing.
- Technology: Achieving high data rates with low latency requires a number of technical changes. India lacks the technical knowhow for the roll out of 5G. She is heavily dependent on foreign manufacturers for 5G equipment to establish networks.
- Security: India is largely dependent on China for equipment imports. However, a 2017 Chinese law makes it mandatory for Chinese companies to share data with their military. This raises fears of potential espionage. India’s data protection regime is still not mature enough to take care of data security and privacy concerns.
- Policy: Lack of a clear policy to incentivize heavy investment on 5G in India. Concern over pricing shifts the focus from long term benefits.
- Interference issues: The spectrum used by 5G will be near that of some remote sensing such as well as weather and Earth observation satellites. Interference to satellite operations impairs weather prediction performance affecting the economy and public safety
- Health concerns: 5G uses higher frequency waves than earlier mobile networks and require more transmitters than previous technologies positioned closer to ground level. So, there is a concern over increased exposure to radiations.
WAY FORWARD:
The shift from 4G to 5G is not incremental in nature, but transformational. Given what it means for the entire ecosystem, skipping it is not a choice India can afford. It is important that India make most of the opportunity and should not lag behind the rest of the world
To ensure that we need to take suitable measures like:
- The availability of affordable and adequate spectrum must be ensured. In addition to the proposed band of 300 MHz, the 26 GHz millimeter wave band spectrum can also be made available for rolling out 5G services.
- A dedicated organization on the lines of ISRO shall be established to develop capacity in communication technologies and hardware development. This will reduce our dependency on foreign equipment which compromises our security. Simultaneously we need to build cyber security architecture to defend against any possible offensives.
- Industry is a vital link in the expansion of communication sector. They must be taken into confidence with a multi stakeholder approach by addressing their various concerns.
- Adequate scientific investigations must be carried out to rule out any adverse health impacts
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q. What is 5G or Fifth Generation? Discuss its significance for India?

