Competition Commission of India
2023 APR 21
Mains >
Polity > Institutions/Bodies > Regulatory bodies
IN NEWS:
- President Droupadi Murmu has given assent to the bill to amend the competition law.
THE KEY CHANGES INTRODUCED BY THE COMPETITION (AMENDMENT) BILL, 2023:
- The bill empowers the Competition Commission of India (CCI) to penalise entities found engaging in anti-competitive behaviour based on their global turnover rather than just their turnover in India.
- The bill affords CCI a greater say in mergers and acquisitions, as entities will have to seek its approval if deals are worth more than Rs. 2,000 crore and if both parties have substantial business operations in India.
- It proposes to expedite CCI clearance of mergers and acquisitions to within 150 days, down from a maximum of 210 days now.
- The Bill decriminalizes certain offences under the Act by changing the nature of punishment from imposition of fine to civil penalties.
COMPETITION COMMISSION OF INDIA:
- Competition Commission of India (CCI) is a statutory body responsible for promoting competition throughout India and preventing activities that have an appreciable adverse effect on competition in India.
- It was established via The Competition Act, 2002 and became fully functional in May 2009.
- Evolution:
- A need was felt to promote competition and private enterprise especially in the light of 1991 Indian economic liberalisation.
- Hence, based on the recommendations of the Raghavan Committee, the Monopolies and Restrictive Trade Practices Act, 1969 (MRTP Act) was repealed and replaced by the Competition Act, 2002.
- Composition:
- CCI consists of a chairperson and 6 Members appointed by the Central Government.
- The commission is a quasi-judicial body.
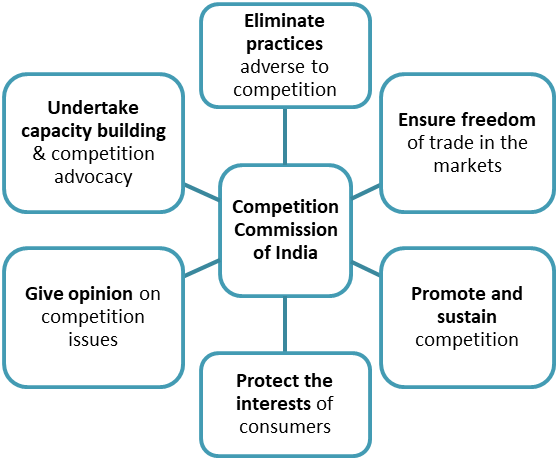
FUNCTIONS:
------------------------------------------ 
WHY IS CCI NECESSARY?
- Promotion of free enterprise:
- Competition laws are described as the Magna Carta of free enterprise. Competition is important for the preservation of economic freedom and our free enterprise system.
- Protection against market distortions:
- Market can suffer from failures and distortions, and various players can resort to anti- competitive activities such as cartels, abuse of dominance etc. This can adversely impact economic efficiency and consumer welfare and hence needs to be regulated.
- Protect consumers’ interest:
- In the era of liberalization, an effective competition commission is essential to ensure fair competition to all kinds of producers and make the markets work for the welfare of the consumers.
- Promote ease of doing business:
- Presence of good competition reduces the need for frequent government interference through regulation of business. This in turn fosters ease of doing business in the country.
- Foster employment and innovation:
- Competition attracts new enterprises, which in turn creates jobs and provides people with a choice of employers and work places.
- Competition among companies can spur the invention of new or better products, or more efficient processes. Antitrust laws of CCI encourage companies to compete so that both consumers and businesses benefit.
- Promote sustainable development:
- Strong competition ensures that the producers make the most out of the resources they have to enhance profit. They invest in cost reduction strategies like modifying the work structure, recycling wastes and streamlining operations.
CRITICISM OF CCI:
- Overlapping functions:
- CCI’s jurisdiction extends to the entire economy including sectors such as banking, capital markets, insurance, telecommunications, roads and ports that already have sector-specific regulatory agencies. Hence, there is frequent regulatory tussle over jurisdiction.
- Emergence of dynamic markets:
- The emerging business models today are based on a digital economy and e-commerce. This model is a problem for the CCI, since the current competition laws talk only of assets and turnovers.
- Inadequate manpower:
- The Act mandates that the CCI should comprise of one chairman and six members. However, in practice, the criteria is rarely met. For eg: As of August, 2021, the commission consists of only the chairman and 2 members.
- Multiple functions:
- The CCI has been vested with adjudicatory, advisory, investigative, quasi-legislative, and advocacy functions. However, the body lacks the resources or capability to handle all of them parallelly.
- Conflict with Intellectual Property regime:
- IPR is usually used as a tool to create exclusive monopoly rights to the holder whereas Competition law seeks to avoid the misuse of the monopoly power.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. Enumerate the functions of the Competition Commission of India (CCI). Discuss its relevance in the contemporary economy?
