Mains > Environment & Ecology > Global warming > Events and functions
Syllabus
GS 3 > Environment > Conservation
REFERENCE NEWS
Recently, the 28th Conference of Parties (COP28) to the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was held in Dubai, United Arab Emirates.
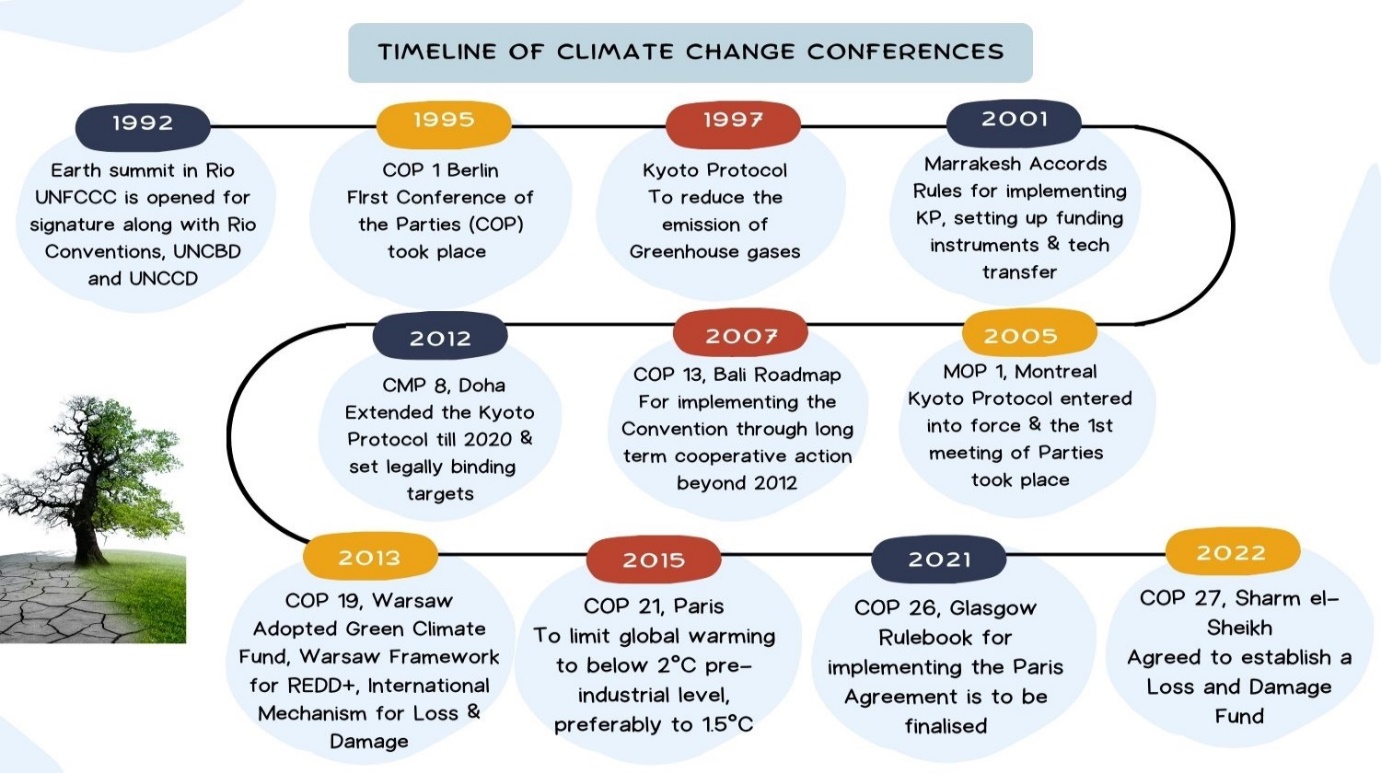
ABOUT COP
KEY HIGHLIGHTS OF COP-28

SIGNIFICANCE AND SHORTCOMINGS
| Initiatives | Significance | Shortcomings |
| Fossil fuel phase-out | The role of fossil fuels in causing global warming had never been even acknowledged in any earlier COP decision. | There were no time schedules and no targets. Some countries were extremely disappointed that the term “fossil fuel phase-out” had not been used. |
| Tripling of Renewable Energy | Tripling along with the doubling energy efficiency has the potential to avoid emissions of about 7 billion tonnes of carbon dioxide equivalent between now and 2030. This is more than the net result of all the other climate actions being currently taken. | Tripling is a global target, and it is not incumbent on every country to individually triple its current installed capacity. It is thus not clear how this tripling would be ensured. |
| Phase-down of coal | Coal has received a separate mention in the agreement. This is because coal was already singled out for phase-down at the Glasgow conference in 2021. There was a move to stipulate that no new coal-fired power plants could be opened without an in-built carbon capture and storage facility | This was strongly resisted by India, China, South Africa and other countries. It was dropped, and finally the Glasgow language was reiterated. There is nothing about how this phase-down is to be measured, or from what baseline. |
| Methane emission cuts | Methane is the most widespread greenhouse gas apart from CO2, accounting for nearly 25 percent of all emissions. It is also about 80 times more potent than CO2 in causing global warming. Methane emission reductions can therefore bring substantial benefits. | Cutting methane emissions could involve tweaking agricultural patterns which could be extremely sensitive in a country like India. Possibly in deference to the concerns of such countries, the agreement does not mention any targets for methane emission cuts for the year 2030. |
| Global Goal on Adaptation | Historically, adaptation hasn’t received enough attention, as compared with mitigation activities which makes the current initiative the first step in the right direction. | The adaptation agreement currently lacks financial provisions, and countries would need to continue working on it to strengthen it in the coming years. |
WAY FORWARD
COP28 highlighted crucial advancements in climate action, particularly in renewable energy and adaptation strategies. Yet, it fell short in setting precise targets and timelines, reflecting the ongoing challenge of balancing global climate ambitions with diverse national interests and capabilities.
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q: Analyze the key outcomes and shortcomings of the 28th Conference of Parties (COP28) to the UNFCCC held in Dubai.(15marks, 250words)