Mains > Security > Cyber Security > Cyber warfare
REFERENCE NEWS
Resecurity, an American cyber security company, said that personally identifiable information of 815 million Indian citizens, including Aadhaar numbers and passport details, were being sold on the dark web.
WHAT IS CYBER SECURITY?
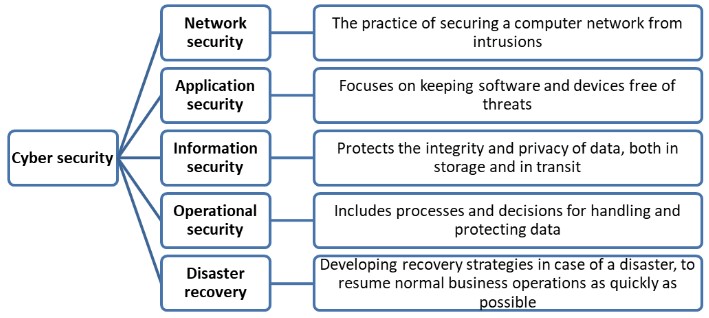
CYBER ATTACKS:
|
Cyber Espionage: |
Refers to the use of computer networks to gain illicit access to confidential information, typically that held by a government or other organization. Ex: The 2019 cyber-attack on Kudankulam nuclear power plant. |
|
Cyber Crime: |
Cybercrime is any criminal activity that involves a computer, networked device or a network.They are carried out to generate profit. Ex: Cosmos Cooperative Bank,Pune ATM Fraud of 2018 |
|
Cyber Terrorism
|
It refers to unlawful attacks and threats of attacks against computers, networks and information stored to intimidate or coerce a government or its people in furtherance of political or social objectives. |
|
Cyber Warfare |
It may be defined as actions by a nation-state or its proxies to penetrate another nation’s computers or networks for the purposes of espionage, causing damage or disruption. It is perceived to be the fifth domain of warfare |
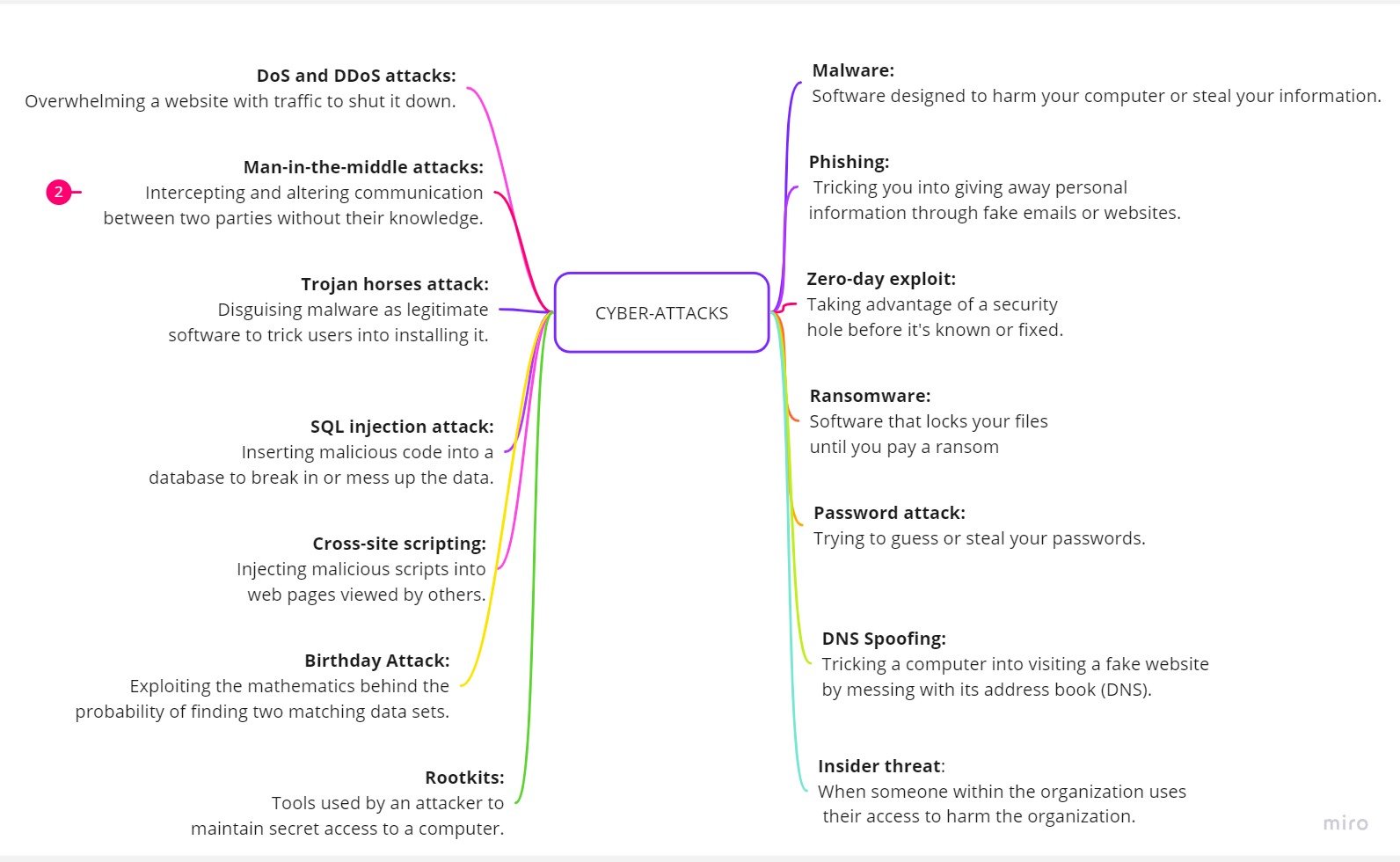
METHODS OF CYBER-ATTACKS
STATISTICS
|
Crime in India report,2021 (NCRB)
|
Cybercrimes recorded an increase of 11.8% in 2020 Cybercrimes have increased four times or 306 percent in the past four years and rate of cybercrime (incidents per lakh population) increased in 2020.
|
|
CERT-In
|
1.16 million cases of cyberattacks were reported in 2020, up nearly three times from 2019 and more than 20 times compared to 2016. Over 26,100 Indian websites were hacked during 2020 |
RECENT EXAMPLES
AIIMS, 2023: The systems at AIIMS and its centers were corrupted by the cyberattack, which wiped outpatient and research data from its primary and backup servers.
Attack on Air India (2021): India's national airline suffered a cyber-attack on its data servers, which affected about 4.5 million customers around the world.
Aadhaar data leak (2019): As recently as February 2019, Aadhaar details of over 6.7 Million users containing details such as names, addresses and the numbers were leaked.
SIGNIFICANCE OF CYBER SECURITY:
Increasing internet use in India:
Increasing digitisation in India
Constitutional obligations:
Increased instances of cyber-crimes:
Critical Infrastructure:
Cost incurred due to cyber-attacks are increasing:
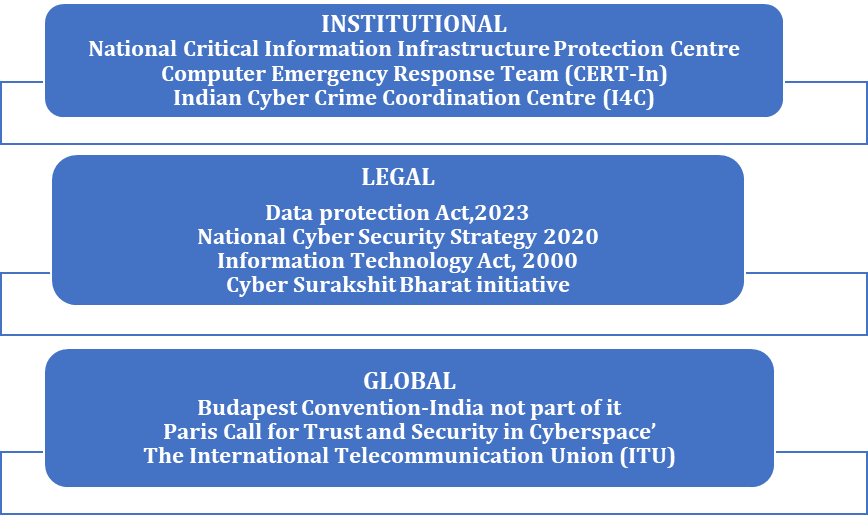
GOVERNMENT INITIATIVES
CHALLENGES TO CYBERSECURITY
Lack of awareness:
Weak digital security:
Issues with India's cyber security institutions:
Lack of resources:
Regulatory mechanism not equipped:
External attacks:
Obsolete systems:
Offshore servers:
Under reporting:
Jurisdictional Uncertainty:
Reliance on Chinese equipment in telecom sector:
WAY FORWARD
CASE STUDY: KERALA’S CYBERDOME PROJECT
Cyberdome is the Kerala Police Department’s premier facility which involves a team of ethical hackers, expert coders, youth prodigies skilled in software, law enforcers and civilian volunteers.
Establish a Central Cybersecurity Agency: Create a single, authoritative national body for cybersecurity to streamline and coordinate national defense efforts.
Update Legal Frameworks: Reform the IT Act, 2000, to cover modern cyber threats, including issues related to cryptocurrencies and IoT.
Enhance Public-Private Partnerships (PPPs): Foster closer cooperation between government and the private sector to enhance cybersecurity infrastructure and intelligence sharing.
Invest in Cybersecurity Education and Workforce Development: Integrate cybersecurity into academic curricula and professional training to address the skills gap.
Implement Cybersecurity Awareness Campaigns: Conduct nationwide programs to educate the public on cyber threats and safe digital practices.
Addressing India's cybersecurity challenges requires a multifaceted and dynamic approach, adapting to technological advances and evolving threats in the digital landscape.
PRACTICE QUESTION
Q: Elaborate on the challenges faced by India’s cybersecurity system? (10M,150W)