Review of India's G20 Presidency
2023 SEP 13
Mains >
International relations > International Institutions > International groupings
IN NEWS:
- The G20 Leaders’ Summit 2023 concluded recently with Prime Minister Narendra Modi handing over the G20 Presidency gavel to Lula da Silva, the President of Brazil, the country that will officially assume the presidency of the grouping on December 1, 2023.
WHAT IS THE G20?
- The Group of Twenty (G20) is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 countries: Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, the Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States, and the European Union(the African Union became a permanent member of the G20 during the Delhi summit in 2023)
- The G20 members represent around 85% of the global GDP, over 75% of the global trade, and about two-thirds of the world population.
- The G20 was founded in 1999 after the Asian financial crisis as a forum for the Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors to discuss global economic and financial issues.
KEY OUTCOMES OF G20 SUMMIT 2023:
- Induction of the African Union as a full member of the G20.
- India’s move to include the African Union as a member of the G20 in June of this year (2023) has paid off. The African Union became a permanent member of the G20 during the Delhi summit in 2023 and will have the same status as the 27-member European Union (EU).
- Launch of a Global Biofuel Alliance with India, the US, and Brazil as founder-members:
- The Global Biofuel Alliance (GBA) is an initiative by India as the G20 Chair.
- The Alliance intends to expedite the global uptake of biofuels through facilitating technology advancements, intensifying utilization of sustainable biofuels, shaping robust standard setting and certification through the participation of a wide spectrum of stakeholders.
- GBA aims to serve as a catalytic platform, fostering global collaboration for the advancement and widespread adoption of biofuels.
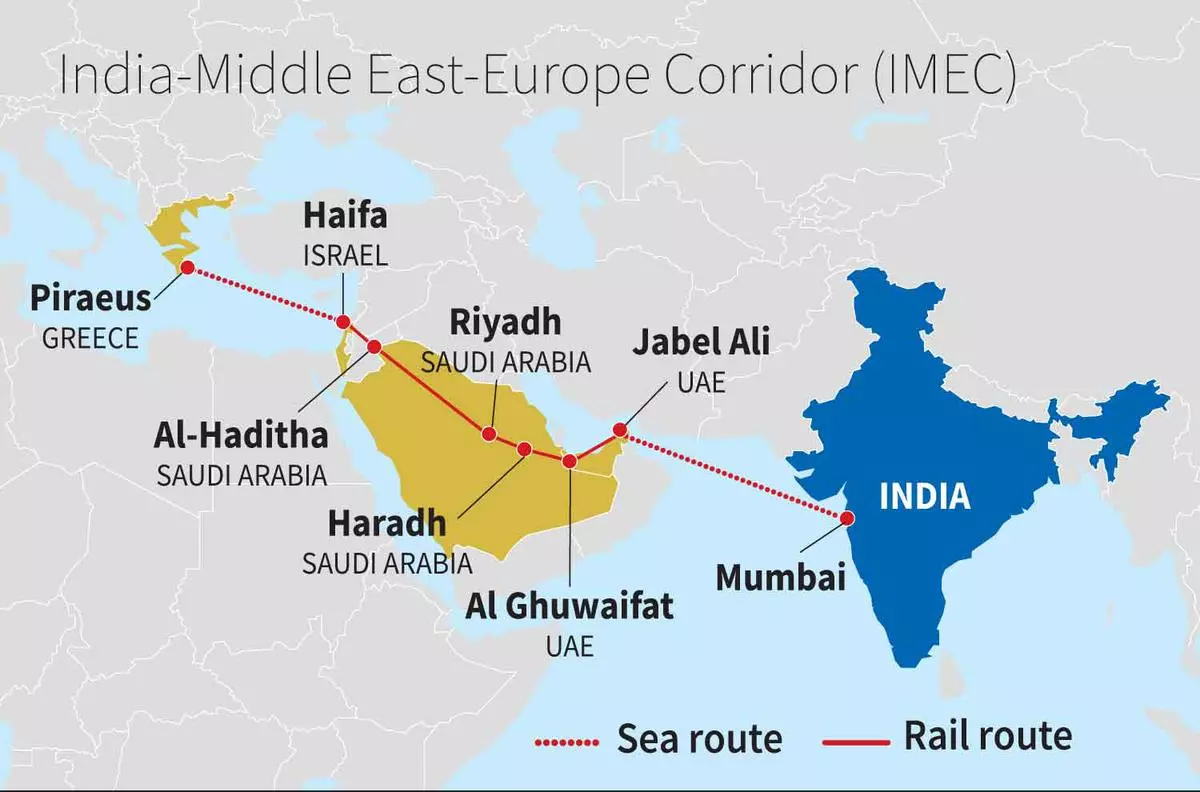
- Announcement of the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor(IMEC):
- During the G20 summit, a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) was signed among the governments of India, the U.S., Saudi Arabia, the European Union, the UAE, France, Germany, and Italy to establish the India-Middle East-Europe Economic Corridor.
- IMEC is envisioned as a network of transportation routes encompassing railways and sea lanes.
- Its primary objective is to promote economic development by fostering integration between Asia, the Arabian Gulf, and Europe.IMEC can make trade between India and Europe faster by an estimated 40 percent.
- The unanimous adoption of the G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration 2023.
- All 83 paragraphs of the 2023 G20 New Delhi Leaders’ Declaration were unanimously approved, achieving a remarkable 100 percent consensus, even with China and Russia in agreement.
- The New Delhi Declaration has impressive coverage, inter alia, of sustainable and inclusive growth, the 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development, international trade, climate change, and finance, improved access to medical countermeasures for health emergencies, debt vulnerabilities, reforms of Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs), and Digital Public Infrastructure.
- The big sticking point was the Ukraine-Russia conflict, which was addressed in detail in seven paragraphs.
- The Delhi Declaration called for a 'just and durable peace in Ukraine. At the same time, the declaration avoided condemnation of Russia over the war in Ukraine.
ACHIEVEMENTS OF INDIA'S G20 PRESIDENCY
- Delhi Declaration: A Diplomatic Win
- It is a diplomatic win for India by building consensus at the G20 summit in Delhi for the New Delhi Declaration.
- G20 India Sherpa Amitabh Kant has said that a 100 percent consensus on the New Delhi Leaders' Declaration is an achievement for India amid an extremely polarized world.
- This was achieved by arriving at the formulation that Russia’s invasion of Ukraine does not need to be explicitly mentioned.
- Unlike the 2022 G20 Bali Declaration, in which Russia was described as the aggressor and asked to withdraw its troops from Ukraine fully and unconditionally, the the New Delhi Declaration refers only to the "war in Ukraine" and notes with "deep concern the immense human suffering and the adverse impact of wars and conflicts around the world.".
- The declaration highlighted India's exceptional ability to act as a crucial bridge between emerging economies, developed nations, Russia, and China, effectively bringing them all to the negotiation table.
- India as the voice of the Global South:
- Though issues of interest to the Global South have all along figured in the G20 agenda, India, at the very beginning of its presidency, gave the Global South a much higher profile by organising the Voice of the Global South summit with participation from 125 countries.
- Also, the issues of concern to the Global South figure right through the New Delhi Declaration.
- The inclusion of the African Union in the G20 is an achievement of India’s Presidency and reflects its commitment to the developmental agenda of the Global South.
-
- The term Global South is used to refer to developing countries in Asia, Africa, and Latin America, while economically developed countries such as the United States, Canada, Europe, Russia, Australia, and New Zealand constitute the Global North.
- India hosted a two-day Voice of Global South Summit on 12-13 January 2023. The Summit was held in virtual format, with 10 sessions in total. It saw participation of Leaders and Ministers from 125 countries of the Global South.
|
- India's permanent membership in the UNSC:
- During the G20 Summit, US President Joe Biden reaffirmed support for India's permanent membership in the United Nations Security Council (UNSC), aligning with India's campaign for reforming global governance structures.
- With India's proposal to include the African Union in the G20 grouping becoming successful, India has pitched itself as the leader of the developing and underdeveloped countries.
- This is also in sync with India’s aspiration for permanent membership in the UNSC, for which Delhi is keen to garner support from Africa, which has 55 votes.
- Democratic approach - "People's G20":
- One of the highlights of India's G20 presidency is its democratic approach. In a break from tradition, international delegations ventured far beyond New Delhi, reaching small towns and cities across the country.
- This was a deliberate move to democratise the G20 process, making it inclusive and representative of every state and union territory and involving communities that have never before experienced such an international event.
- As Prime Minister Modi said, India's G20 presidency has become the "People's G20", as crores of peoples are connected with it.
- In more than 60 cities across the country, more than 200 meetings have taken place as part of India's G20 presidency.
- Multilateral Institutions for the 21st century:
- India's G20 presidency always gave priority to reformed multilateralism that creates a more accountable, inclusive, just, equitable, and representative multipolar international system that is fit for addressing the challenges of the 21st century.
- As per the New Delhi Declaration 2023, the leaders committed to pursue reforms for better, bigger, and more effective Multilateral Development Banks (MDBs), such as the International Monetary Fund, World Bank, Asian Development Bank, etc., to address global challenges and maximise developmental impact with a continued focus on addressing the development needs of low- and middle-income countries.
- Climate change:
- Climate change is a key priority of India’s presidency. As the issue of climate change cuts across industry, society, and sectors, India presented the world with LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment), a behaviour-based movement to adopt environmentally-conscious practices.
- During its presidency, India has made various efforts to make LiFE a global movement for a green lifestyle.
- The theme of India’s G20 Presidency “Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam” or “One Earth · One Family · One Future” closely ties with LiFE (Lifestyle for Environment).
- Also, the Global Biofuel Alliance launched during the G20 summit 2023 was an important step towards more research and delivery of alternative energy sources in a world still dependent on fossil fuels.
- Gender Equality and Women Empowerment:
- India’s collective and unwavering dedication to championing 'Gender Equality and Empowering All Women and Girls' has now secured a firm place within the G20 New Delhi Declaration 2023.
- Leaders of the G20 agreed to the creation of a Working Group on the empowerment of women to support the G20 Women’s Ministerial which will convene its first meeting during the Brazilian G20 Presidency.
- Technological Transformation and Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI):
- The Delhi summit focused on Technological Transformation and Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), thus providing India with an opportunity to showcase its considerable accomplishments in these areas.
- Virtual "review" meeting:
- India’s proposal to hold a virtual "review" meeting in November 2023 before India gives up its presidency would provide a chance to ensure implementation and scrutiny of the decisions made at the 2023 G20 summit.
CHALLENGES:
- China’s silent presence:
- Chinese President Xi Jinping’s decision to stay away from the G20 summit and downgrade China’s participation to the level of Premier Li Qiang was a sign that despite the bonhomie of the consensus at the Delhi Declaration, the world’s geopolitical divide remains.
- Implementation of New Delhi Declaration:
- The 83-paragraph New Delhi Declaration has impressive coverage, from sustainable and inclusive growth, climate change, and finance to Digital Public Infrastructure. Its transformational capacity is, however, dependent on its implementation.
- The revitalization of multilateralism:
- The Delhi Declaration calls for the revitalization of multilateralism, making global governance more representative, and enhancing the representation and voice of developing countries in decision-making in global economic and financial institutions.
- However, the resistance of entrenched interests to such reforms in the UN and international financial institutions is well known. In sum, though an ambitious declaration has been put together under the Indian presidency, much work lies ahead for G20 countries to ensure its implementation.
- Outcomes of G20 meetings are non-binding:
- The G20 meetings are never seen as transformative. After all, it is a premier forum for leaders to deliberate on the unfolding challenges and major crises across countries. It needs to be stressed that the outcomes of G20 meetings are neither binding on the G20 members nor on the international multilateral bodies.
- African Union is still dependent on foreign support:
- The African Union is still too dependent on foreign support, which makes up 65 percent of its budget. Experts raise concerns about how it can occupy the G20 seat and make its own choices without budgetary sovereignty.
CONCLUSION:
- As the leadership of the G20 passes to future presidencies, India's legacy stands as a paradigmatic example of diplomacy's potential to shape a more equitable and sustainable global order, reaffirming its pivotal role on the international stage.
PRACTICE QUESTION:
Q. “The outcomes of the G20 Summit will bolster India’s claim to be the voice of the global south and reaffirm its pivotal role on the international stage.” Analyse critically.
